What is TPU?
TPU, or thermoplastic polyurethane, is a type of thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) commonly used by manufacturers in the automotive, transportation, aerospace, sporting goods, and medical device industries. TPU combines the high durability of plastic parts with the elasticity of rubber parts, making TPU ideal for applications where it needs to be repeatedly bent or compressed.
Due to its elasticity, TPU is often used as an impact modifier for products like helmets, protective packaging, anti-vibration products, and gaskets or seals. TPU also has excellent abrasion resistance and is relied upon in high friction or environments like car interiors or for electrical cables and insulators. For applications in these industries where oil is often present, TPU can be relied upon for its resistance to oil stains as well.
How Are TPU Parts Made?
TPU products are ubiquitous in everyday life, and their popularity makes them ideal for mass production, most commonly through traditional injection molding processes. Many products that we think of as rubber are actually TPU.
Injection molding is a cost-effective way of producing parts in mass quantities but has limitations in terms of geometric flexibility or customization. Injection molded parts are standardized in order to be produced in quantities of hundreds of thousands to millions — so for industries like medical device manufacturing or sporting goods, there is a demand for alternatives that lend themselves better to low volume production or customization.
Mass production also inhibits small businesses and startups from getting their products to market quickly, because they’re reliant on large industrial injection molders for external production.

Introducing TPU 90A Powder for Flexible, Tough, and Skin-Safe SLS Parts
Watch our webinar to learn how TPU 90A Powder can help you bring soft-touch, rubber parts in-house with Fuse Series 3D printers.
Why 3D Print TPU?
3D printing TPU and TPE materials presents opportunities outside of traditional workflows for parts with greater geometric complexity, personalized or customized designs, more rapid iteration and design, and more cost-effective low-volume production.
There are various options for TPU 3D printing, including fused deposition modeling (FDM) and selective laser sintering (SLS) technologies. As 3D printing technology and materials have advanced, the number of manufacturers incorporating this workflow into their process has grown exponentially.
TPU 3D printing enables a shorter iterative cycle for rapid prototyping applications, as well as customization possibilities for end-use part production. In industries where one phase of the product development process is traditionally outsourced (typically the mass production manufactuing phase), 3D printing can enable an improved and vertically integrated end-to-end workflow.
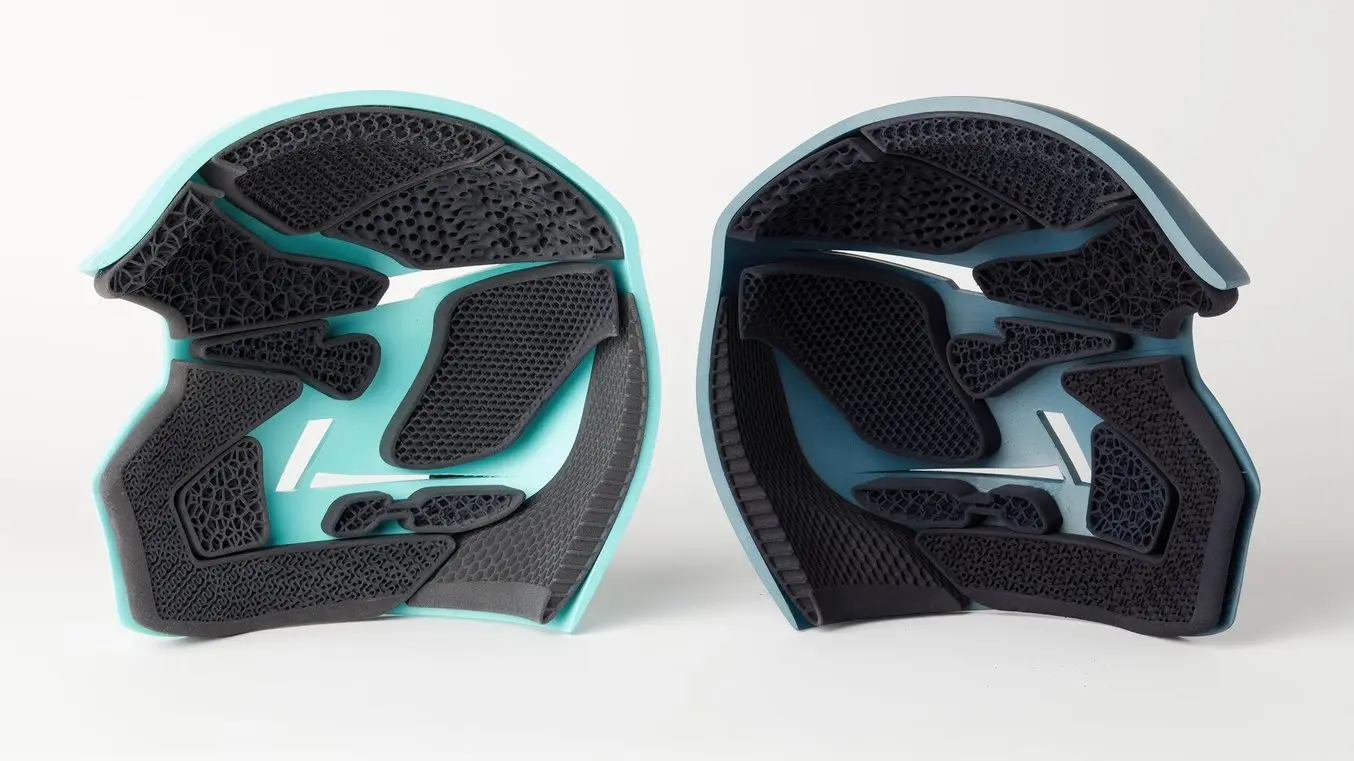
3D printing TPU can also help manufacturers meet the demand for customized and personalized goods. According to a study by Deloitte, in some categories, more than 50% of consumers expressed interest in purchasing customized products or services, with the majority of them willing to pay more for a customized product or service. For applications in which TPU and rubber are commonly used, such as protective devices like helmets or orthotics and insoles, 3D printed TPU parts are perfect for mass-customized helmet paddings, orthotics, sports equipment, goggles, headsets, or ergonomic gripping components for tech products.
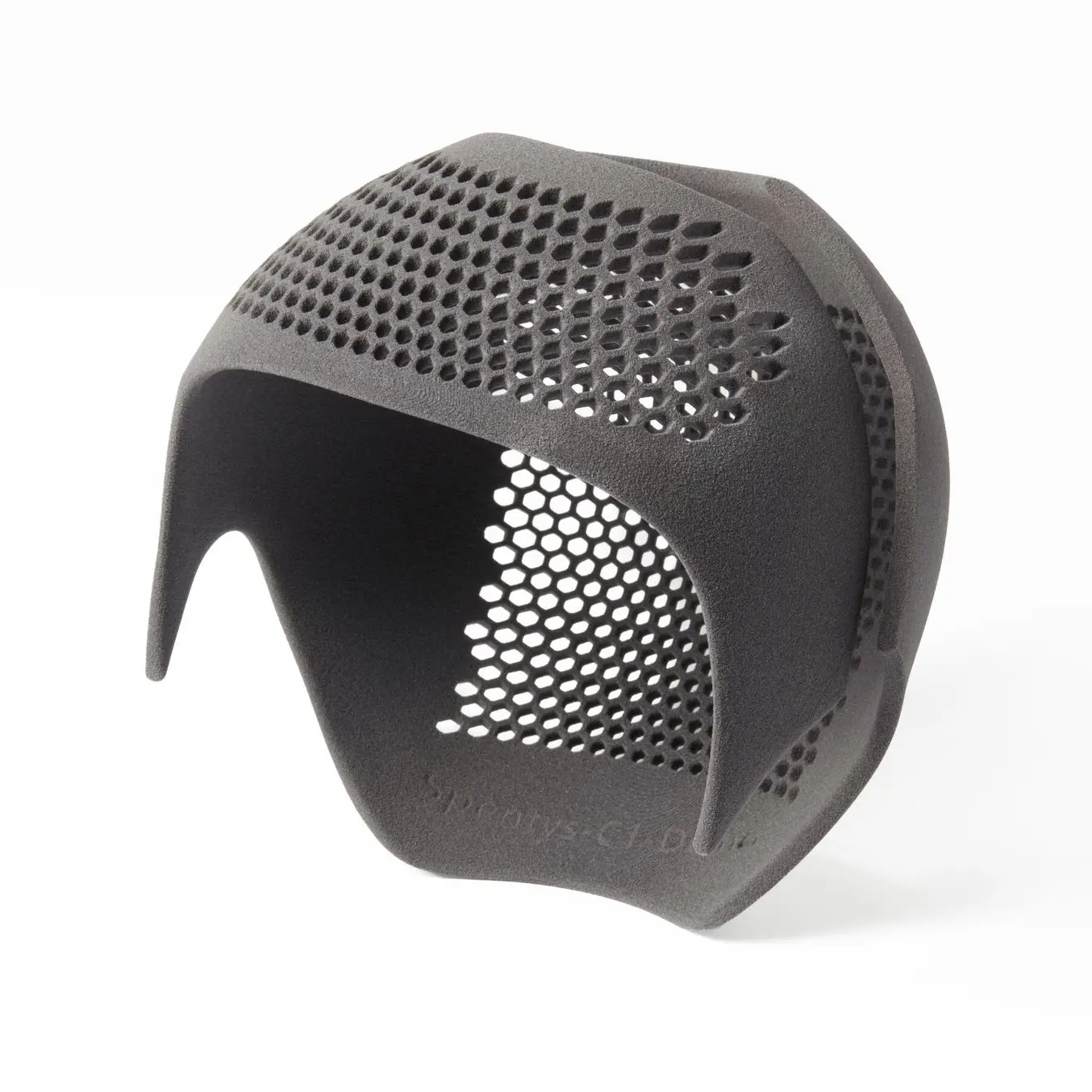

TPU 90A Powder from Formlabs enables customization based on anthropometric data, for applications like this personalized protective head covering.
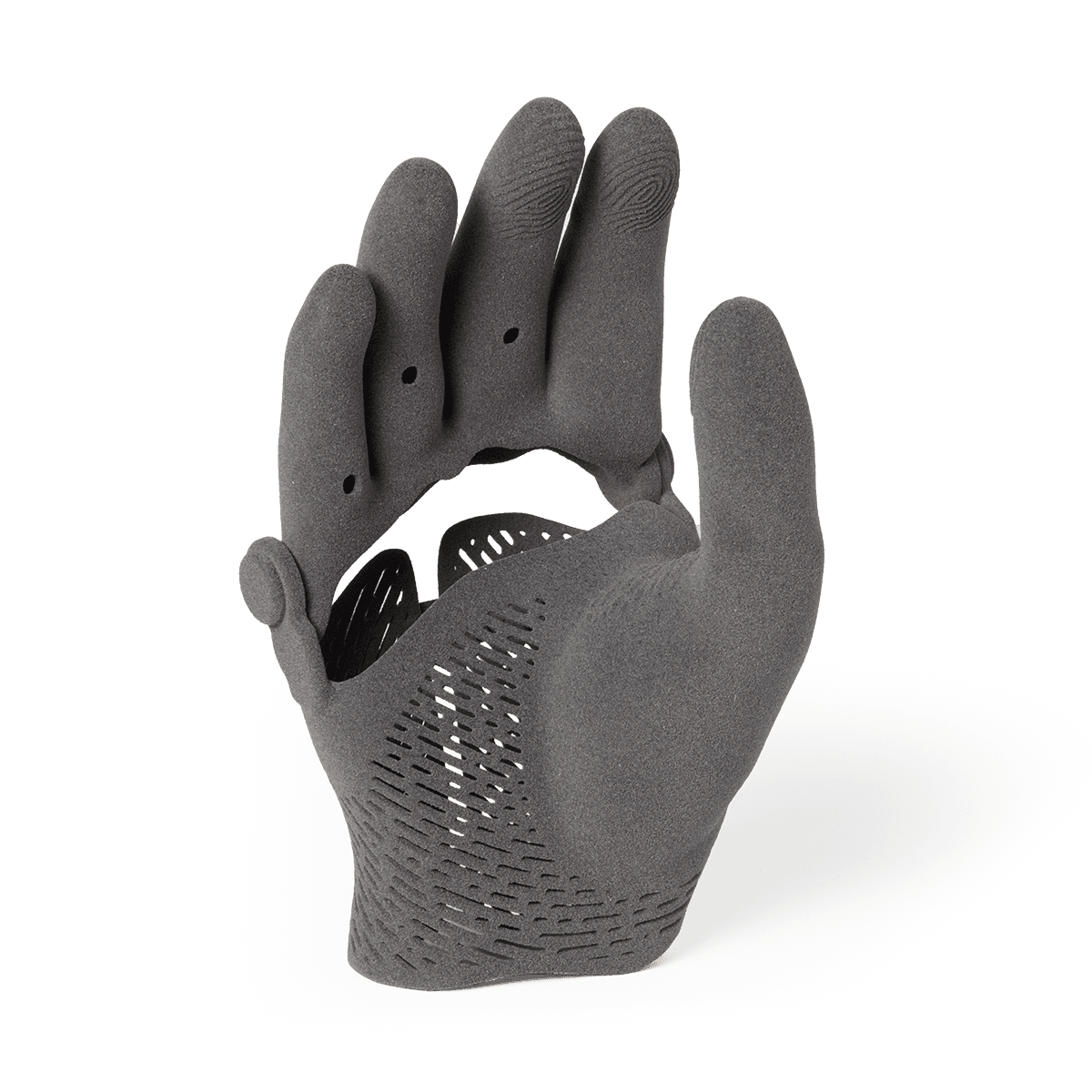

This prosthetic hand covering printed in TPU 90A Powder is flexible, strong, and durable.
How to 3D Print With TPU
TPU can be 3D printed on either FDM or SLS 3D printers. Each technology has unique advantages, and before choosing a technology, it is important to determine what is best for your own workflow and business needs.
| FDM TPU 3D Printing | SLS TPU 3D Printing | |
|---|---|---|
| Functional Material Strength | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★★ |
| Resolution | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★☆ |
| Accuracy | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★★ |
| Surface Finish | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★☆ |
| Throughput | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★★ |
| Complex Designs | ★★☆☆☆ | ★★★★★ |
| Ease of Use | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ |
| Pros | Low-cost consumer machines and materials Fast and easy for simple, small parts | Functional, strong, isotropic parts Production-level throughput Self-supported designs Excellent design freedom |
| Cons | Parts are anisotropic and not watertight or functionally strong Limited design freedom | Slightly rough surface finish |
| Applications | Low-cost rapid prototyping Basic proof-of-concept models | Functional prototyping Low volume production of end-use parts: automotive gaskets, seals, manifolds, consumer goods, shoes, prosthetics and orthotics |
3D Printing TPU With FDM 3D Printing
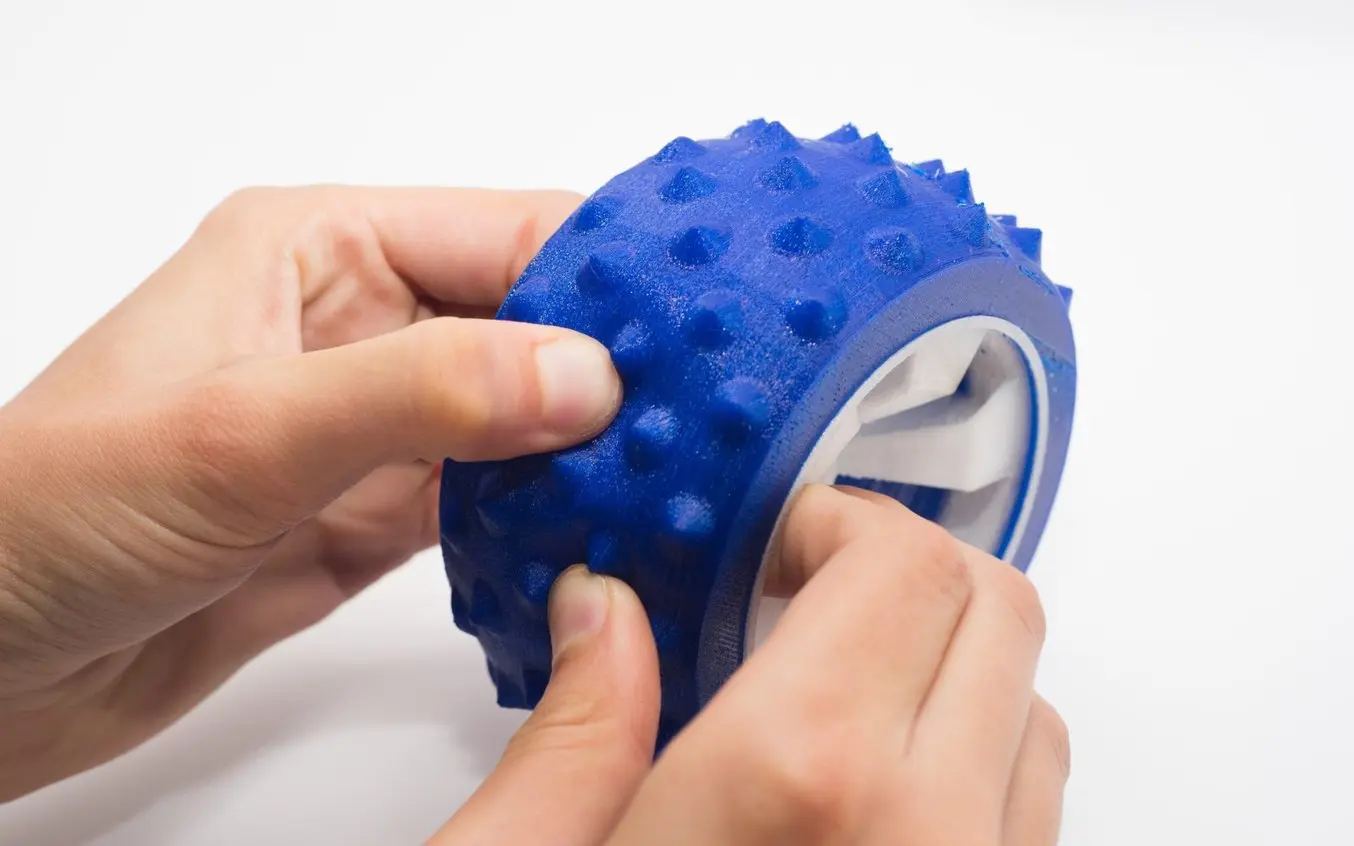

TPU 3D printing on FDM printers is a good entry-level option, but the material is challenging to 3D print and comes with design limitations. (Image source: Hubs)
For businesses looking to start 3D printing TPU, a low-cost FDM printer is a good option for an entry-level workflow. FDM TPU filament is inexpensive and can be a good way to prove out design concepts and looks-like prototypes, especially if the end goal is mass production through traditional injection molding methods.
However, TPU can be a challenging material to 3D print with on FDM printers as the soft and stretchy filament can easily clog the extruder, resulting in technical issues and a lower print success rate. 3D printing TPU on FDM printers also offers limited design freedom, less dimensionally accurate parts, and visible layer lines.
FDM printed TPU parts are anisotropic, meaning their strength is not equal across different axes or planes of stress — in other words, applying force to an FDM printed TPU part in one direction would have a different effect than applying the same force from another direction. For TPU parts, which often need to be pulled, stretched, compressed, and twisted, this anisotropy poses a real challenge for any part that needs to be functional, even in the prototyping phase.
TPU Filaments for FDM Printers
Many FDM printer and material manufacturers offer TPU filaments with varying material properties. FDM TPU filaments are generally a bit harder elastic materials, offering around Shore 95A hardness, but this can be adjusted by tweaking the print parameters or the design.
3D Printing TPU With SLS 3D Printing
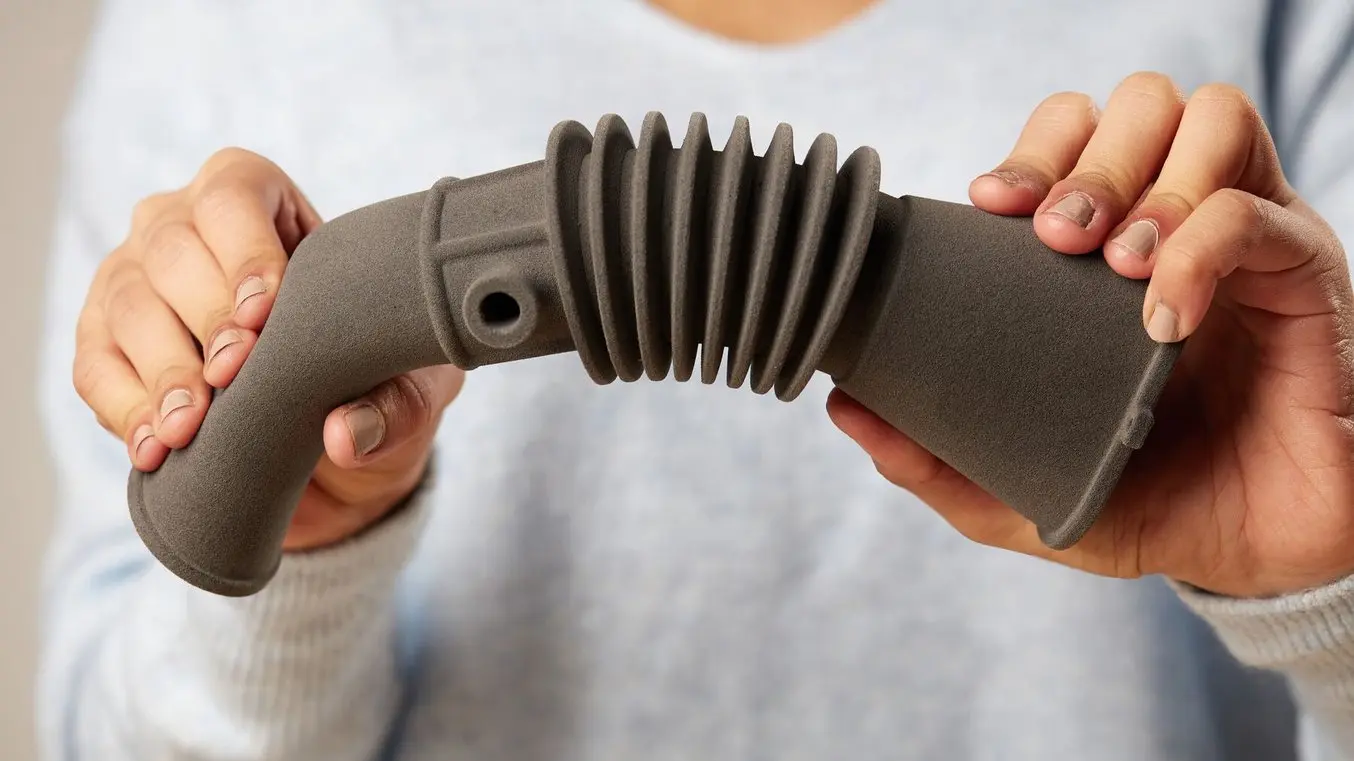
SLS 3D printing technology is ideal for higher throughput and more functional applications, such as functional prototypes for testing or low volume production of customizable end-use goods like orthotics, helmet paddings, and wearables. SLS 3D printing users can leverage TPU’s exceptional strength and flexibility to bring their products to market faster or transform patient care. The high tear strength makes strong, durable, elastomeric parts, and the accessibility of the benchtop SLS systems, like the Fuse Series, enables a low cost-per-part. Additionally, the low refresh rates add to the affordability and scalability of the system, as they increase the efficiency of powder usage and reduce spending on new materials.
SLS 3D printed TPU parts are perfect for applications where complex geometries are necessary or helpful for performance. The self-supporting nature of SLS technology means that no support structures are needed, and intricate geometries with internal channels, latticing, or manifold-type accordion structures are possible. In applications like protective headwear or footwear insoles and orthotics, rubbery lattice structures enable high compressive strength that adds to the effectiveness of the product.
TPU Materials for SLS Printers
There are multiple selective laser sintering (SLS) systems that offer a TPU powder material. Many of these systems are large industrial machines with complicated infrastructure requirements, such as ventilation systems, a large footprint, or multiple circuit and electrical requirements. With the introduction of more accessible SLS systems like the Fuse Series from Formlabs, 3D printing TPU on powder-bed systems is more accessible and affordable.
Formlabs’ TPU 90A Powder is skin safe, opening up opportunities in the wearables and medical device fields, where safety regulations limit the use of many 3D printed parts. With TPU 90A Powder, engineers and designers can utilize the design freedom of 3D printing, the high tear strength and elongation strength of rubber, and the skin-safe qualities of many traditionally molded thermoplastics, all in one workflow.
3D printing TPU with Formlabs’ TPU 90A Powder and the Fuse Series SLS printers is simple, and can easily integrate into an existing SLS workflow, or be the first SLS material you start with. The material prints in an air environment and does not require an inert atmosphere, which some SLS materials do.
Additionally, TPU parts don’t use Surface Armor (the semi-sintered shell around parts in stiffer powders) on Fuse Series printers, so the depowdering process is quite simple using the Fuse Sift post-processing machine. While TPU 90A doesn't have Surface Armor, media blasting is still recommended to remove all excess powder from the parts, providing a cleaner and easier material to work with. Switching a current Fuse Series printer to TPU 90A is absolutely possible, though Formlabs recommends a dedicated Fuse Sift, and build chamber.
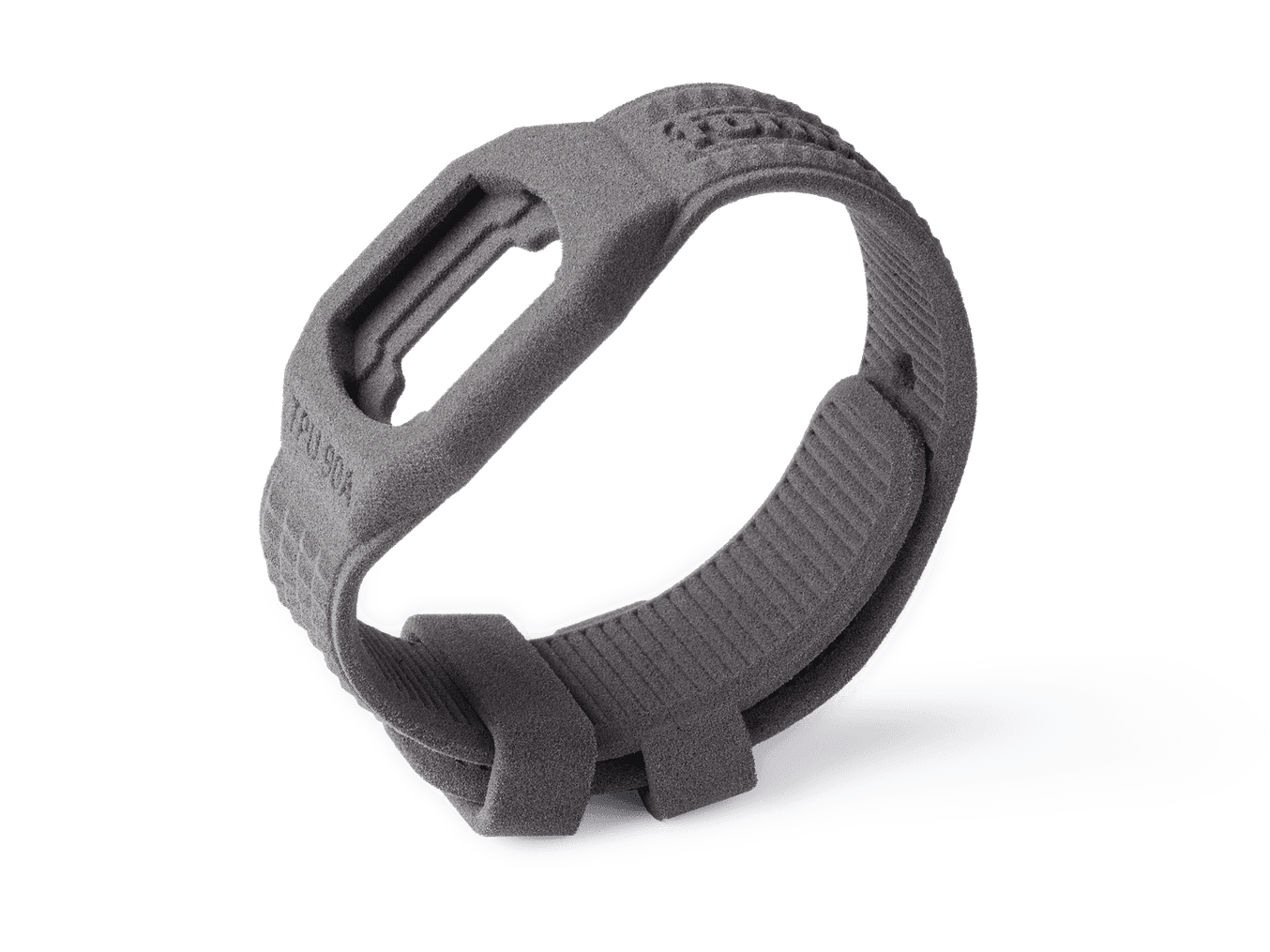

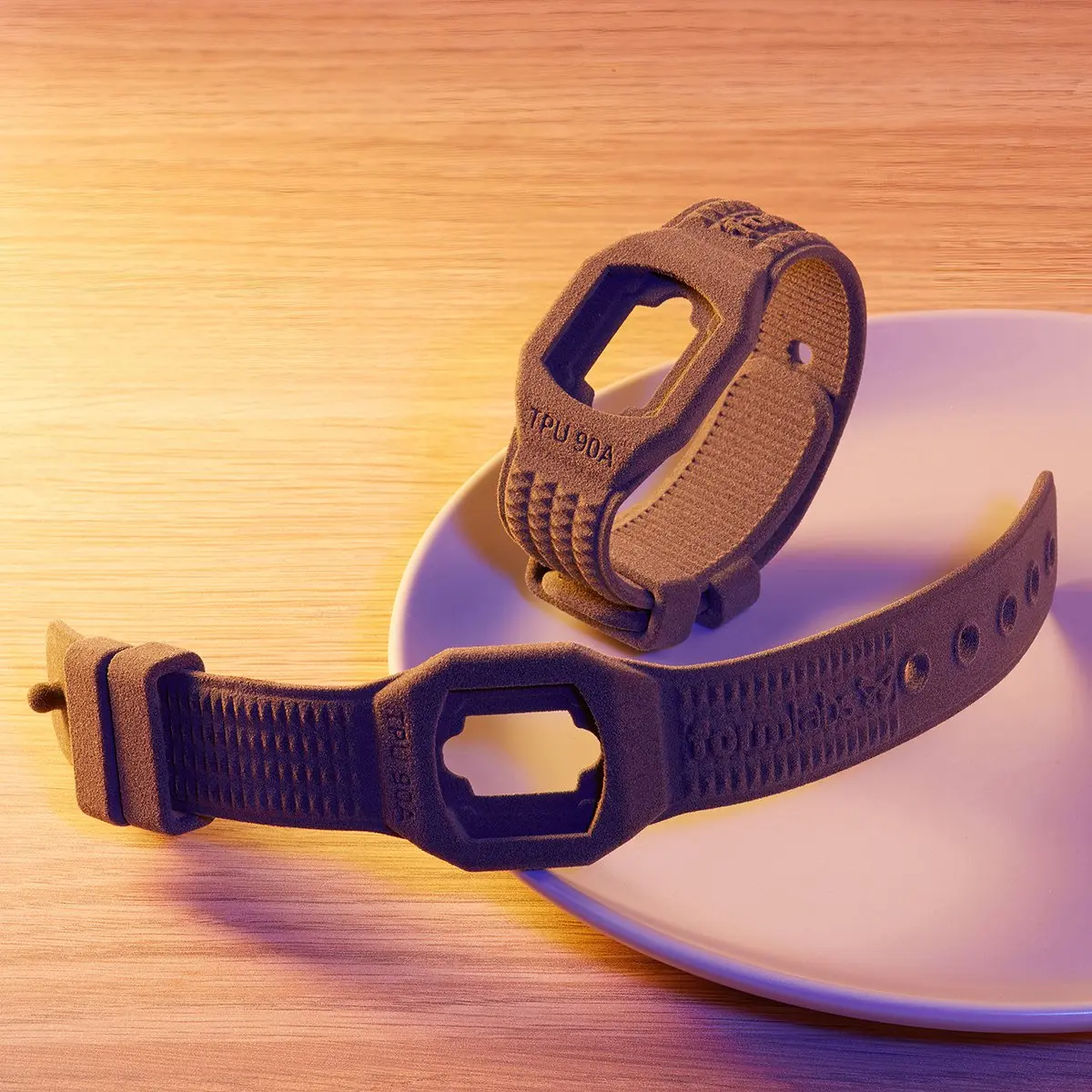
TPU 90A: Formlabs’ Flexible SLS Powder
Request a free sample watch-strap printed in TPU 90A Powder, our first flexible SLS material.
Applications of TPU 3D Printing
There are proven workflows for the traditional manufacturing of TPU parts, and these workflows are still ideal for mass-produced rubber products. However, 3D printing TPU is a great alternative in many situations, including where speed or ease of use is necessary, rapid prototyping, on-demand manufacturing aids, and customization applications. From the beginning of a design process where quick prototypes are necessary to final designs for end-use parts, even mass customized consumer goods, 3D printed TPU can make workflows faster and more efficient, without sacrificing mechanical properties or fidelity.
Rapid Prototyping
3D printing with TPU enables businesses to bring prototyping capacity under their own roof, cutting down lead times and reducing costs previously charged by service bureaus or machine shops.
Prototyping a sports helmet, for instance, requires the ability to fabricate a hard shell as well as the soft cushioning inside. Innovative companies are working to design new lattice structures and impact negation technology for those cushions, and TPU is a perfect material.
Experimenting with new designs and geometries, however, makes traditional tooling methods prohibitively expensive, and outsourcing to design bureaus can take weeks. Being able to use one workflow and one type of technology for the hard outer shell as well as the soft inner cushion means these innovators can iterate at a much higher rate. These helmets will have to undergo extensive physical testing, so ten cushioning pads will be needed for a single round of testing. These volumes are too high for meticulously hand-crafting a cushioning surface, but too low for traditional TPU molding to be cost-effective. The answer is in-house 3D printing.
Fuse Series SLS 3D printers can easily print multiple rubber lattice structures in TPU 90A Powder, with slight variations to test different designs. By altering the design of the part itself, like changing wall thickness, you can produce parts with varying levels of hardness for different applications or as iterations after testing.
The Fuse Series workflow gives you access to multiple materials covering a wide range of mechanical properties, allows you to keep development and manufacturing all in-house, and manage the design of many different types of components with one technology. TPU 90A Powder unlocks a whole new type of product that can be directly prototyped through 3D printing, with the same trusted Fuse Series platform.

TPU 90A Powder is ideal for prototyping functional prototypes for parts that require flexibility, like skin-safe wearables, performance sports equipment, or shoe insoles.
Manufacturing Aids
If you’re not in the business of making things, the distinction between types of manufacturing aids might be hard to parse. The bottom line, however, remains the same whether you’re talking about a jig, a bracket, an enclosure, or one of the many other ways machines are held together — when you need it, you really need it. TPU is the answer to a problem many manufacturers face: how to prevent their million-dollar manufacturing technology from experiencing too much wear and tear.
Soft-touch manufacturing aids can help extend the lifetime of heavy machinery by cushioning certain impacts or providing the perfect-shaped gripper. When seals or gaskets tear after years of repeated use, the operator can print a replacement instantly and have the manufacturing line back up and running in hours, rather than wait days or weeks for a new part.
Adding material capability is more insurance for manufacturers — it protects them from the broken part or faulty machine component they didn’t see coming. The more mechanical properties they can rely upon in-house, the more they insulate themselves from supply chain delays and high costs of repairs from OEMs. With rubber 3D printed parts, a whole new subset of equipment components can now be repaired or replaced on demand. Avoiding a factory line or process shut-down can save thousands of dollars a day.
TPU can be used for vibration dampers in automotive and aerospace testing, as well as jigs for industrial processes like thermoforming uniquely shaped parts. In automotive factories, large robotic systems operate on gantries that have to bend and swivel. Customized cushions and soft enclosures can help these machines avoid friction and lengthen their lifetimes.

Having TPU material on-hand means that flexible replacement parts and manufacturing aids can be designed and printed same-day, so production never has to stop.
Low Volume and Custom Ready-To-Wear Products
In the sports, fashion, and wearable technologies industries, offering personalization options is imperative for brands looking to capture more market share. The costs associated with tooling made low-volume or one-off production almost impossible, until accessible 3D printing opened up the door.
Still, most 3D printed materials have been too rigid for the sporting goods or wearable market, until TPU. From shoe soles that can be customized to a person’s exact footprint and weight distribution, to football helmets engineered for impact negation, to a watch band molded to your wrist, the possibilities are limitless.

American football helmet with customized paddings printed in TPU on a Fuse Series SLS 3D printer.
Medical Devices
Offering exceptional durability and toughness, 3D printed TPU is ideal for prosthetics, orthotics, patient-specific appliances, and medical devices. Being able to 3D print flexible and strong end use parts creates new opportunities for medical professionals by combining the high tear strength and elongation-at-break of rubber materials with the design freedom and durability of SLS 3D printing.
TPU is a flexible elastomer, making it ideal for 3D printing medical parts such as:
-
Medical device prototypes and end-use medical devices and components
-
Orthotic pads and prosthetic liners
-
Wearables, seals, bumpers, and tubes
-
Splints, cranial remolding helmet
-
Athletic and corrective insoles
3D printing in healthcare, though a burgeoning field, is limited by strict material requirements — both their safety certifications as well as their strength and mechanical properties. 3D printed TPU opens up more opportunities for different applications within healthcare, offering just one more tool in the toolbox.
This custom-made orthotic thumb brace provides greater flexibility and more control than a traditional brace to support and prevent further injury.

TPU is ideal for a wide range of orthotic devices, like foot orthotic liners, as well as athletic and corrective insoles.
Case Studies
Protective Machine Components at Global Printing Press Leader Heidelberg
Heidelberger Druckmaschinen AG is the leading global manufacturer of offset printing presses, operating in over 170 countries with close to 10,000 employees worldwide. The company produces a wide range of tools and automation solutions for the entire printing value chain, from some of the largest and fastest state-of-the-art printing presses to cutting and folding machines.
They use their Fuse 1+ 30W SLS 3D printer to create machinery components, including lightweight parts for pick-and-place robots, new parts for folding machines, and replacement parts for machine components previously manufactured in steel. TPU 90A Powder allows them to create flexible parts that can withstand impact and are malleable enough to fit onto existing rigid machinery.
Because replacement parts or manufacturing aids need to fit onto existing robotics systems, the parts often have strange, complex shapes. They are developed specifically for the application based on the stresses and forces they are subject to, and will undergo consistent wear and tear. The 3D printed parts are also often combined with other components, like metal bearings or Teflon-coated components, that offer anti-friction properties. Some parts are less complex, but still require high accuracy or delicacy.
Flexible TPU parts are used to prevent contamination, shield sharp edges, protect sensors, or prevent wear. SLS 3D printing with TPU 90A Powder is a perfect workflow for this type of part and can protect expensive machinery from the damage associated with such rigorous use.
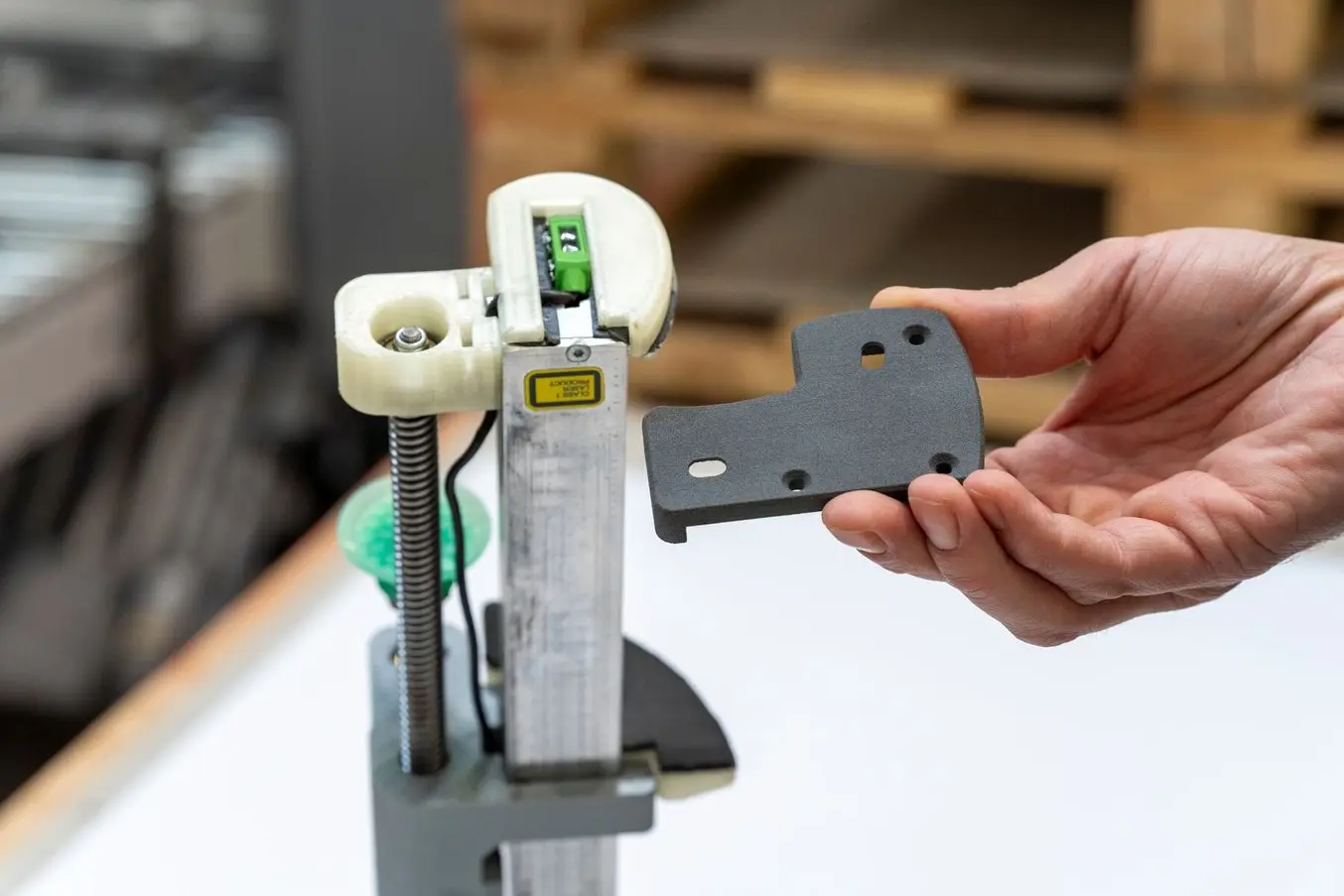

A flexible part printed in TPU 90A Powder to protect sensors and other end-of-arm tooling.
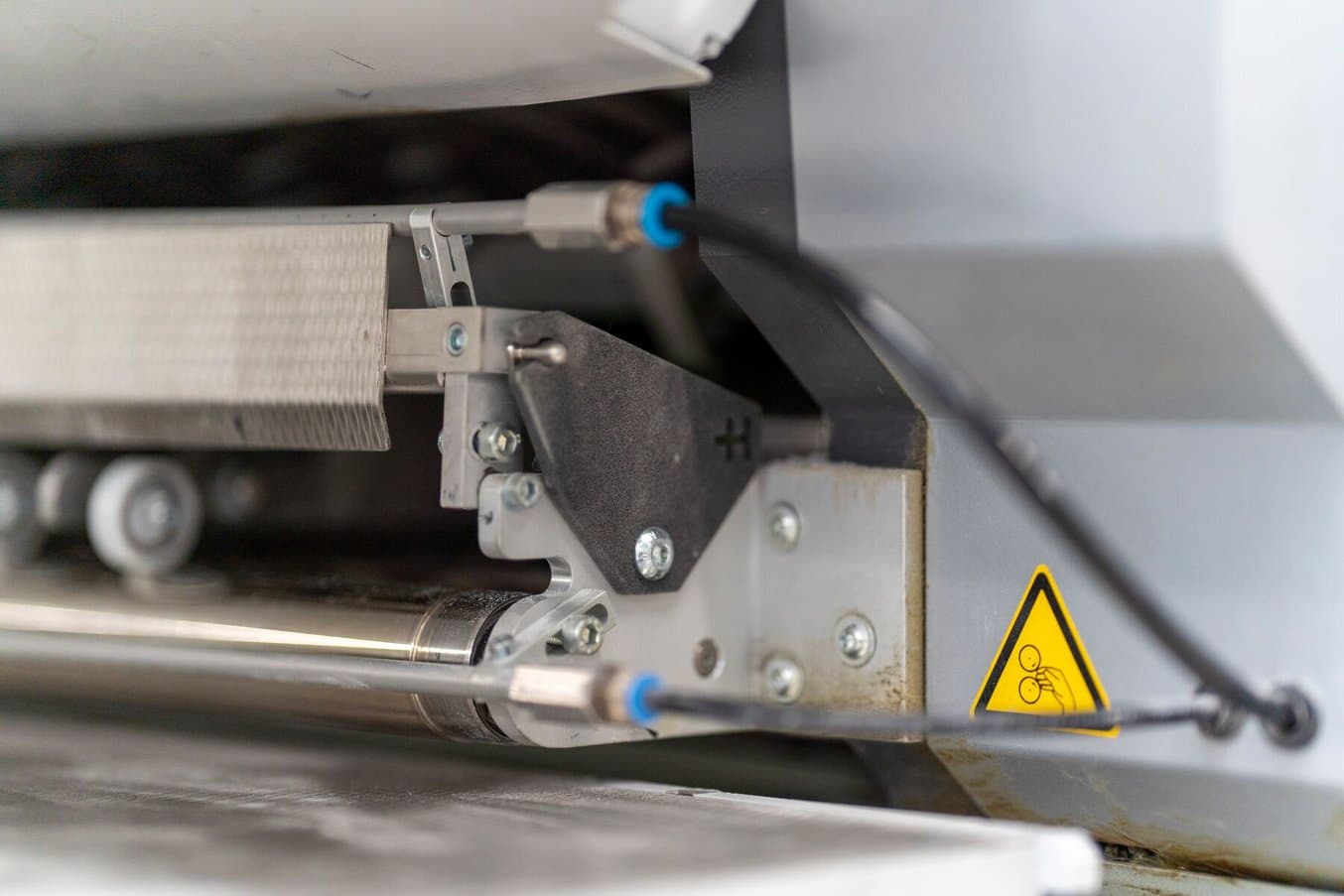

Flexible parts are ideal for snap-fit components. By shielding sharp edges, they also protect operators.
One specific part — a cable guide component printed in TPU 90A Powder —- protects electrical cables from being exposed to a high degree of friction, improving the cables’ longevity and minimizing downtime. If one of these cables snaps or frays, the entire machine is down until a replacement can be ordered and installed. Protective machine components like this cable guide can help keep a factory running.
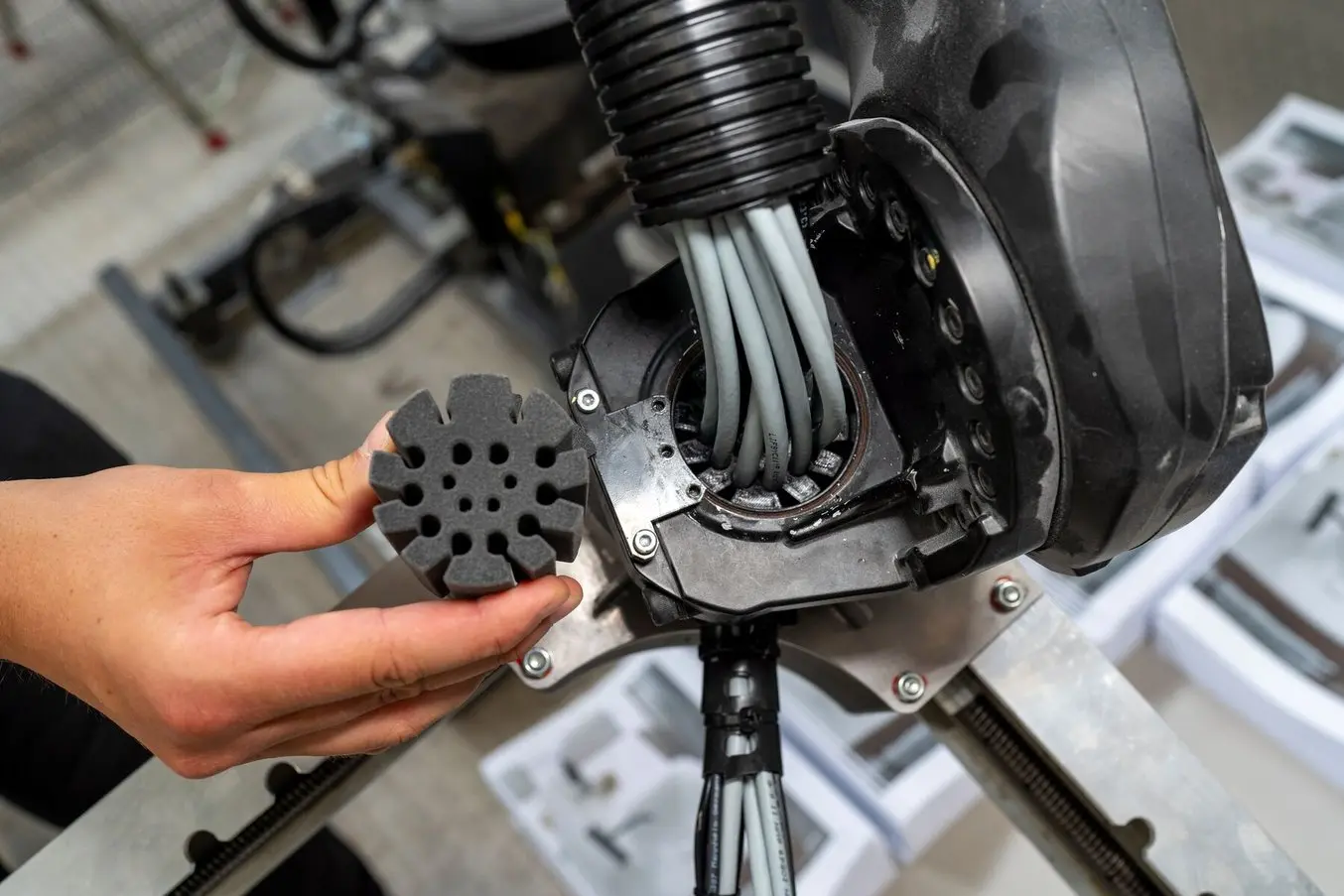
This flexible cable guide produced with a Fuse Series SLS 3D printer enables a complex design and offers a long-term durable solution for protecting the cables from wear.
The accessibility and affordability of the Fuse Series and TPU 90A Powder make it possible for the company to take control of its own supply chain and maintenance needs. TPU 90A Powder parts are ideal for protecting machinery, improving components’ longevity, and ultimately helping the operation reduce costs and avoid downtime.
How Deutsche Bahn Keeps Trains Running With TPU Manufacturing Aids
Deutsche Bahn’s vehicle maintenance location in Neumunster is responsible for overhauling and maintaining Germany’s public trains, and 3D printing helps make their operations as efficient as possible. As a result of integrating 3D printing into their workflow, Deutsche Bahn has saved millions of Euros and shortened lead times for operational train cars to get back on the tracks.
Carsten Wolfgramm, Manufacturing Engineer and Additive Manufacturing Expert, oversees two Fuse 1+ 30W SLS 3D printers — one runs Nylon 12 Powder and the other runs TPU 90A Powder. “We use Formlabs machines because the price-performance ratio is unbeatable for us. They are reliable and really plug-and-play, especially the SLS printers. This makes the job a lot easier when you’re continuously iterating parts. They run 24 hours a day, seven days a week, all year round,” Wolfgramm says.
In one common maintenance operation, technicians remove luggage racks to repaint and re-foil train car walls. Moving the racks around would frequently cause damage to the walls, undoing all the work the maintenance team had just done. To protect the walls, DB’s team designed and 3D printed custom covers for the racks in TPU 90A Powder. The covers slide onto the racks and insulate the edges so that during the removal and replacement they cannot cause any damage to the freshly painted train interiors.
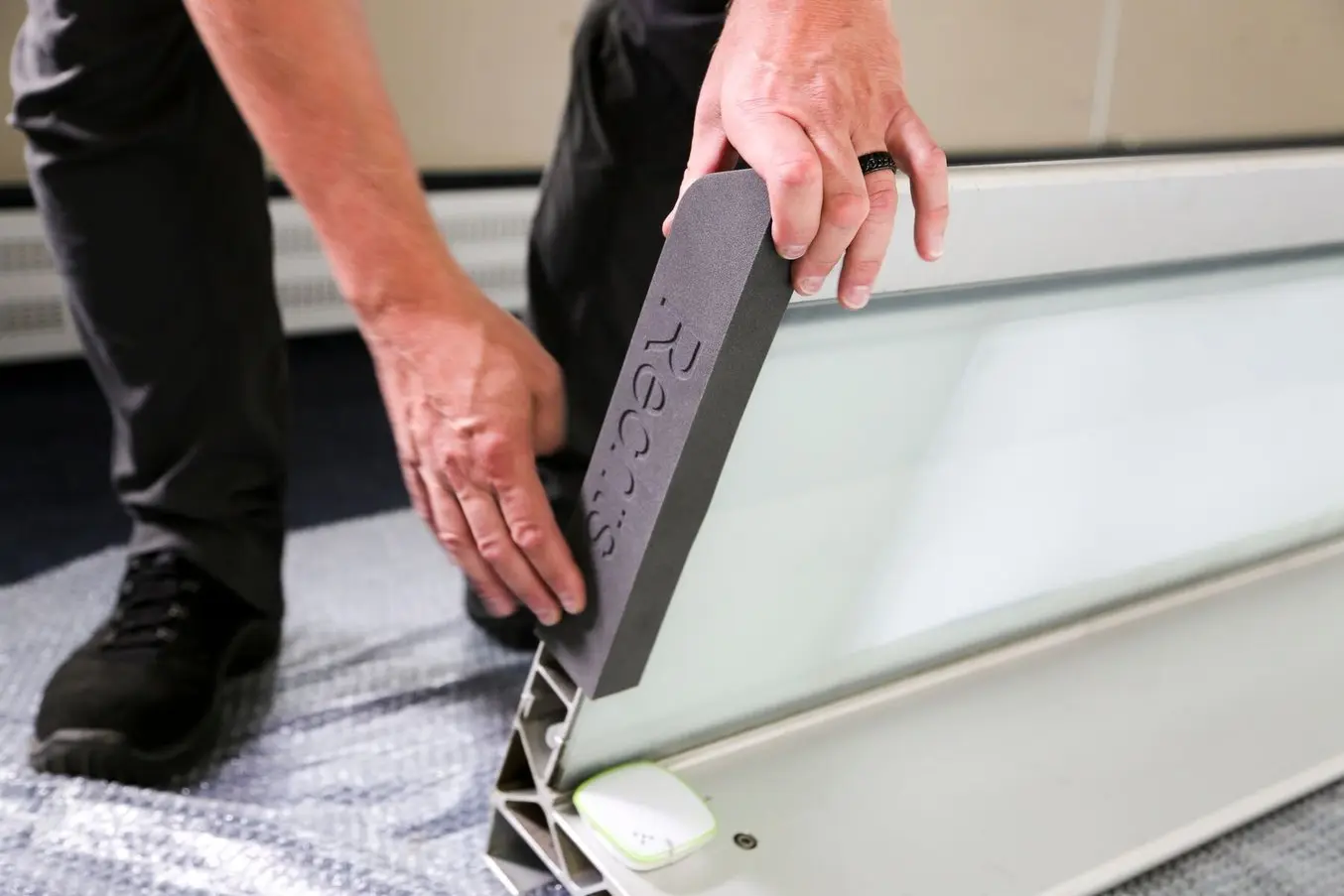

A flexible material, TPU 90A Powder, is used by the team for scratch and impact protection.
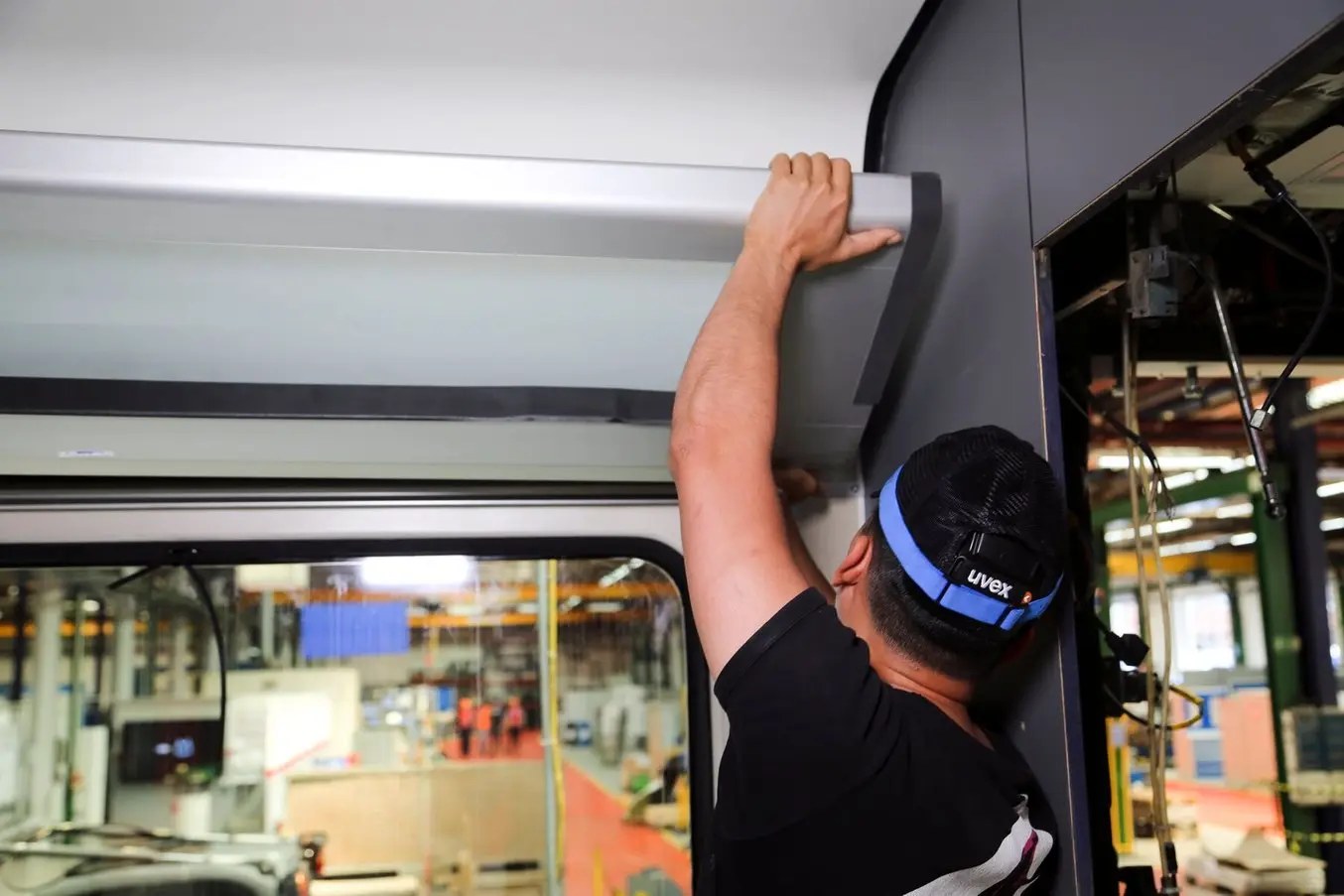

SLS 3D printing enables a slim design that can fit between the luggage rack and the wall.
"Before we developed this scratch protection and 3D printed it, our colleagues always masked it conventionally with bubble wrap or similar tools to try to avoid scratches — but this was not always successful. It’s the first time that we finally managed to completely eliminate scratches thanks to the new TPU parts."
Carsten Wolfgramm, Manufacturing Engineer and Additive Manufacturing Expert, Deutsche Bahn
By demonstrating the cost savings and minimized labor time made possible with 3D printed MRO parts like these, Deutsche Bahn is offering a blueprint for large transportation companies to integrate 3D printing into their workflows. Access to in-house fabrication of customizable flexible 3D printed parts like these protective covers enables Deutsche Bahn to make their processes more efficient and get trains back onto the tracks sooner.
Prototyping at an American Toy & eBike Company: Radio Flyer and TPU
Trusted and loved by families for over 100 years, Radio Flyer is the maker of the iconic Original Little Red Wagon®, which was inducted into the National Toy Hall of Fame. They have stayed at the forefront of popular culture and the top of every child’s Christmas list as the world’s leading producer of ride-on toys including wagons, scooters, tricycles, go-karts, electric bikes, and other innovative products that help families imagine all the places they’ll go.
3D printing is a big part of Radio Flyer’s development process, and design engineer Agostino Lobello has found that TPU 90A Powder helps enable truly functional prototyping. “The high-grip surface finish is unique compared to other 3D printed TPE/TPUs I’ve interacted with. From that standpoint, it does feel more similar to our injection molded TPE/TPU which is exciting from a prototype application. Currently, the next best alternative to this process would be a prototype tool and injecting actual TPE or other urethanes so this is both more cost and time effective,” says Lobello.
"We are excited about the prospect of using this material for tire treads, hand grips, bumpers, seat cushions, and as a way to prototype TPE springs with a specific spring-rate."
Agostino Lobello, Design Engineer
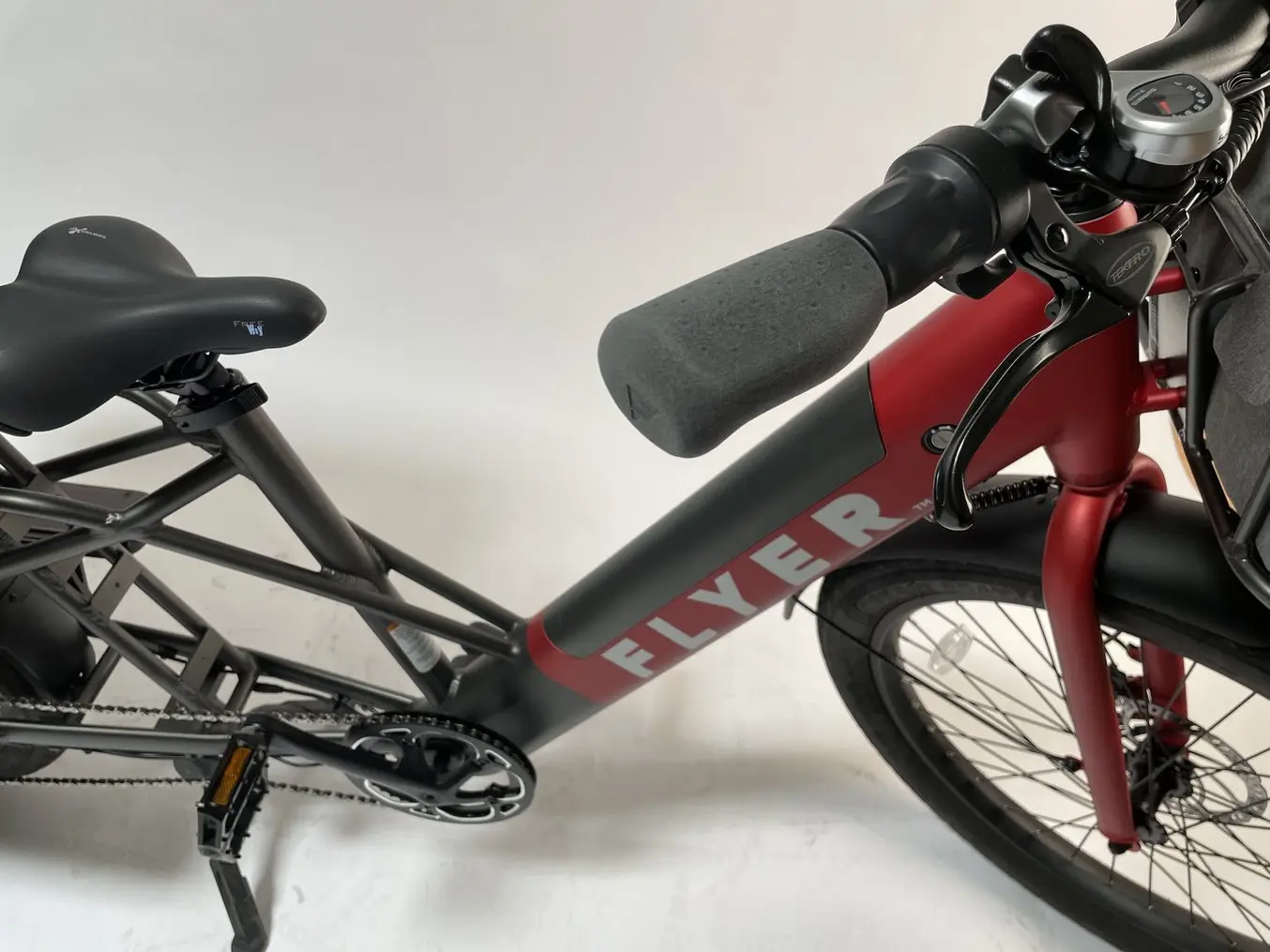

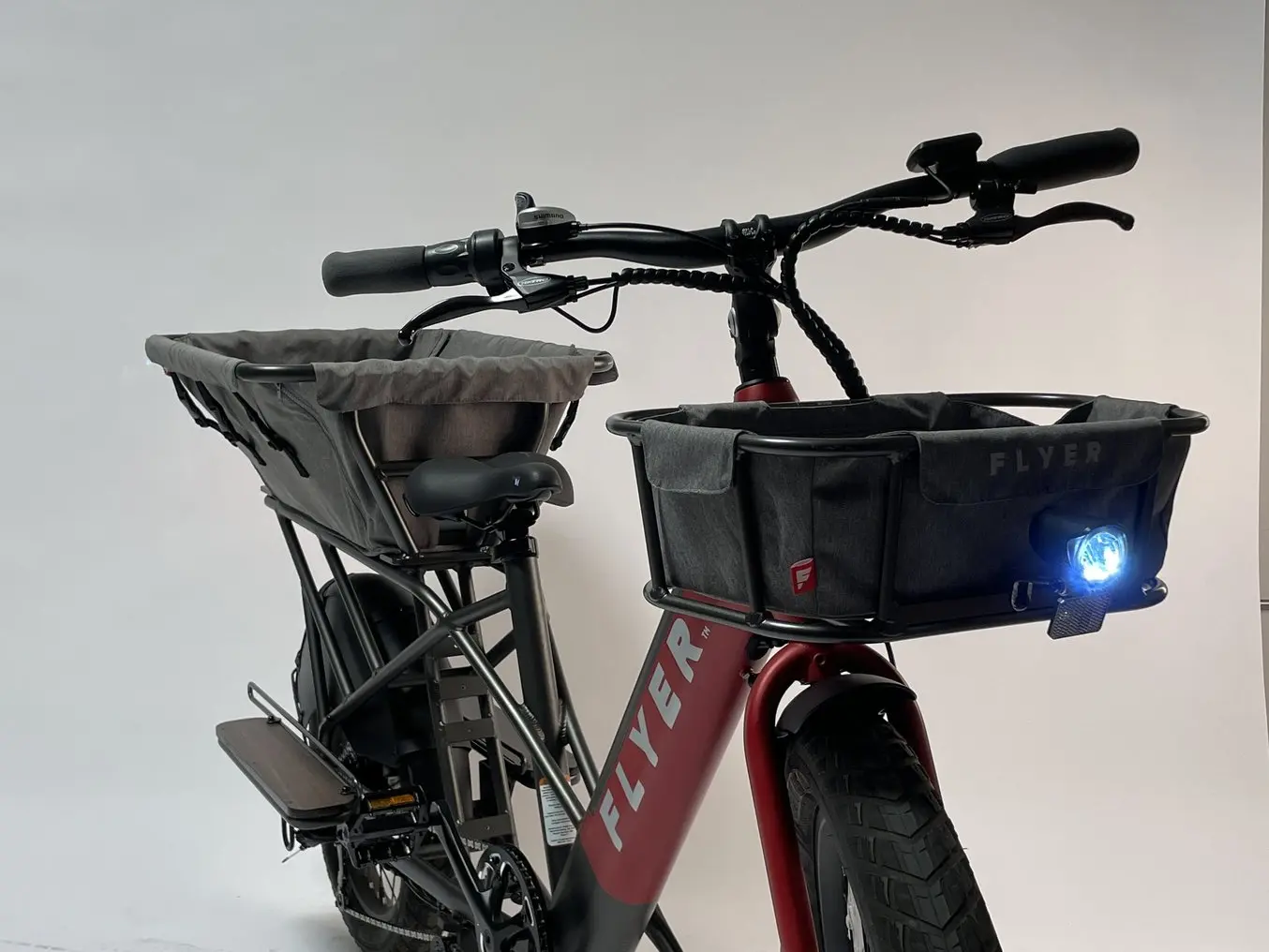
Using TPU 90A Powder on the Fuse Series printers helps Radio Flyer functionally prototype parts like these soft-grip handlebars on their Flyer™ L885 Family Cargo eBike.

Get Started With 3D Printing TPU on the Fuse Series
An accessible SLS 3D printing workflow with TPU powder opens up possibilities for manufacturers to improve their design process through high-quality iterative prototyping, or to engage in customized end-use part production.
The Fuse SLS ecosystem, including printers and the Fuse Sift, is compact, affordable, and accessible. Formlabs TPU 90A Powder enables new applications and streamlines workflows through the creation of strong, flexible, and isotropic parts that previously needed to be molded. In-house fabrication solutions for rubber-like parts give you more control and flexibility in your design and manufacturing process, no matter which application or industry you’re a part of. Formlabs’ TPU 90A Powder has a skin-safe rating, which further opens up possibilities for the healthcare and wearables industries.
To learn more about producing 3D printed TPU parts with the Formlabs SLS workflow, you can request a free sample of our TPU 90A Powder or contact our sales team to discuss your unique application.


