Looking for a high resolution 3D printer? “Resolution” is an often discussed but seldom understood value in the world of 3D printing and additive manufacturing. How does XY and Z resolution influence on the quality of your 3D prints? What's minimum feature size and what layer thickness should you choose?
In this comprehensive guide, you'll learn how 3D printer resolution affects your 3D prints and how it differs between SLA, FDM, and DLP 3D printers.
Resolution vs. Minimum Feature Size
Technology has been in a resolution war for decades. Televisions recently quadrupled pixel counts from HD to 4K and are poised to do it again soon to 8K. Cell phones, tablets, and anything with a screen will have its resolution as the lead on the spec sheet, provided that it’s something to boast about. But this is nothing new. Resolution wars have been waged since digital technology became popular, and the printing industry was one of the first battlegrounds.
If you were around in the 80’s and 90’s, you remember Canon, Brother, HP, Epson, and Lexmark (among others) battling it out for print speed and resolution. What started at 100x100 dots per inch (DPI) quickly escalated to 300x300, then 600x600, and finally the current industry standard of 1200x1200 DPI. Back then, the meaning of these values was clearly understandable; even the units made perfect sense. Unfortunately, things get more complicated when you add another dimension to printing.
3D Printing Resolution
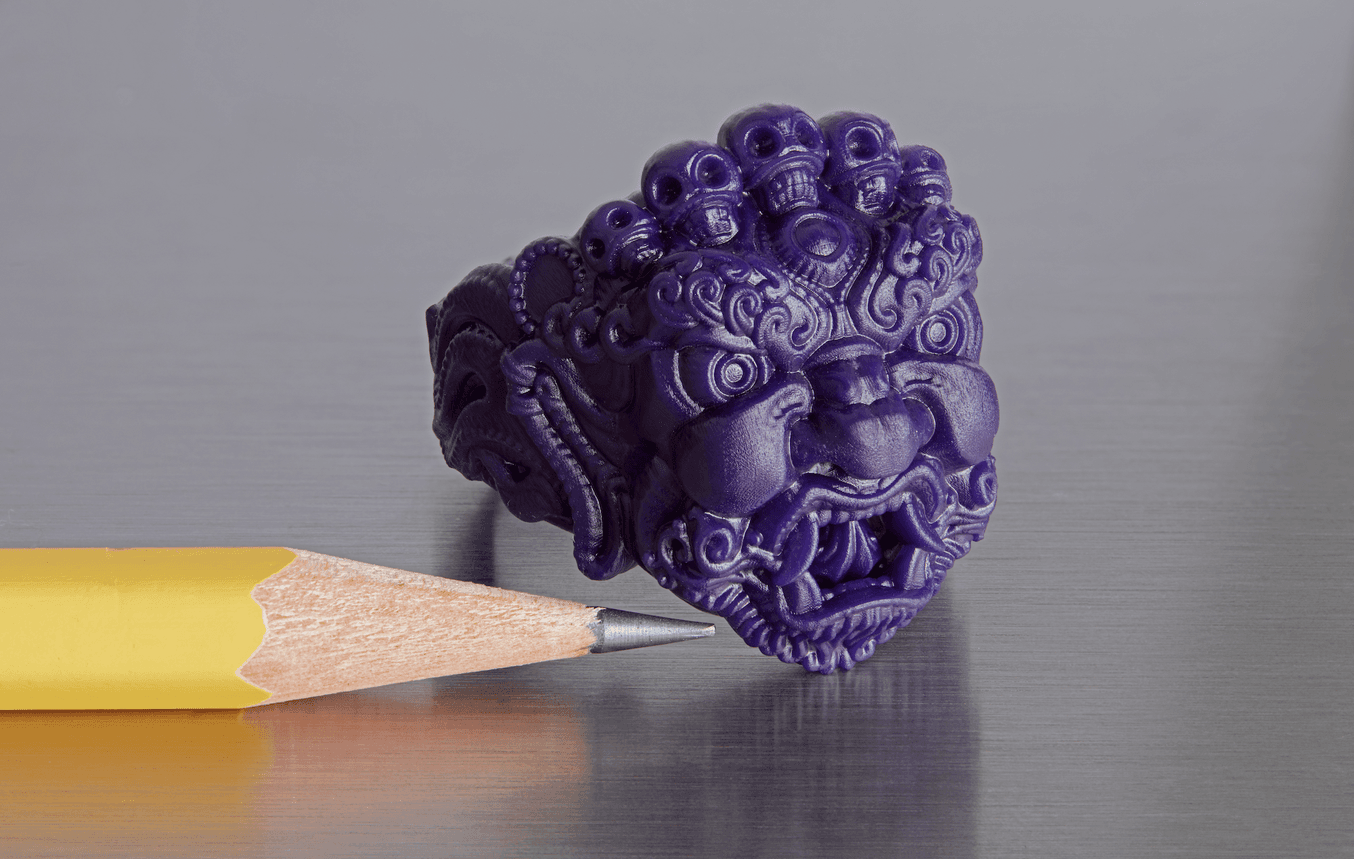

A print’s level of detail is impacted by the 3D printer's resolution in all three dimensions.
In 3D printing and additive manufacturing, there are three dimensions to consider: the two planar 2D dimensions (X and Y) and the Z dimension that makes it 3D printing. Since the planar and Z dimensions are generally controlled via very different mechanisms, their resolutions are going to be different and need to be treated separately. As a result, there is a lot of confusion about what the term “3D printing resolution” means and what level of print quality to expect.

Request a Free Sample Part
See and feel Formlabs quality firsthand. We’ll ship a free sample part to your office.
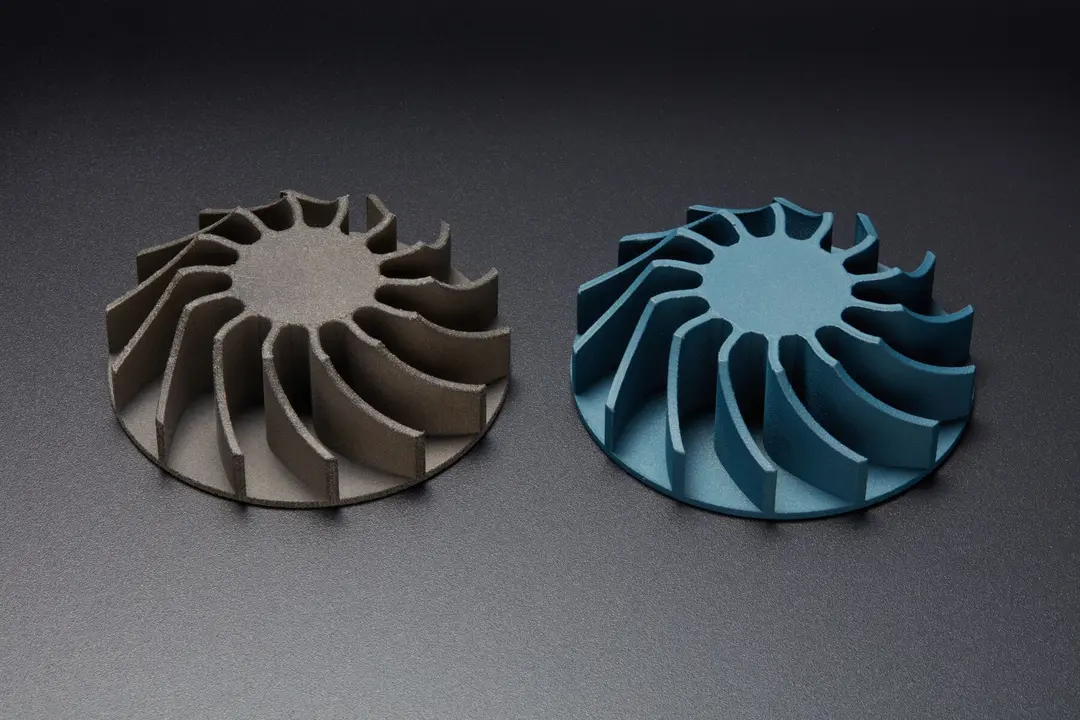
High Resolution 3D Printing - Compare Different 3D Printing Processes
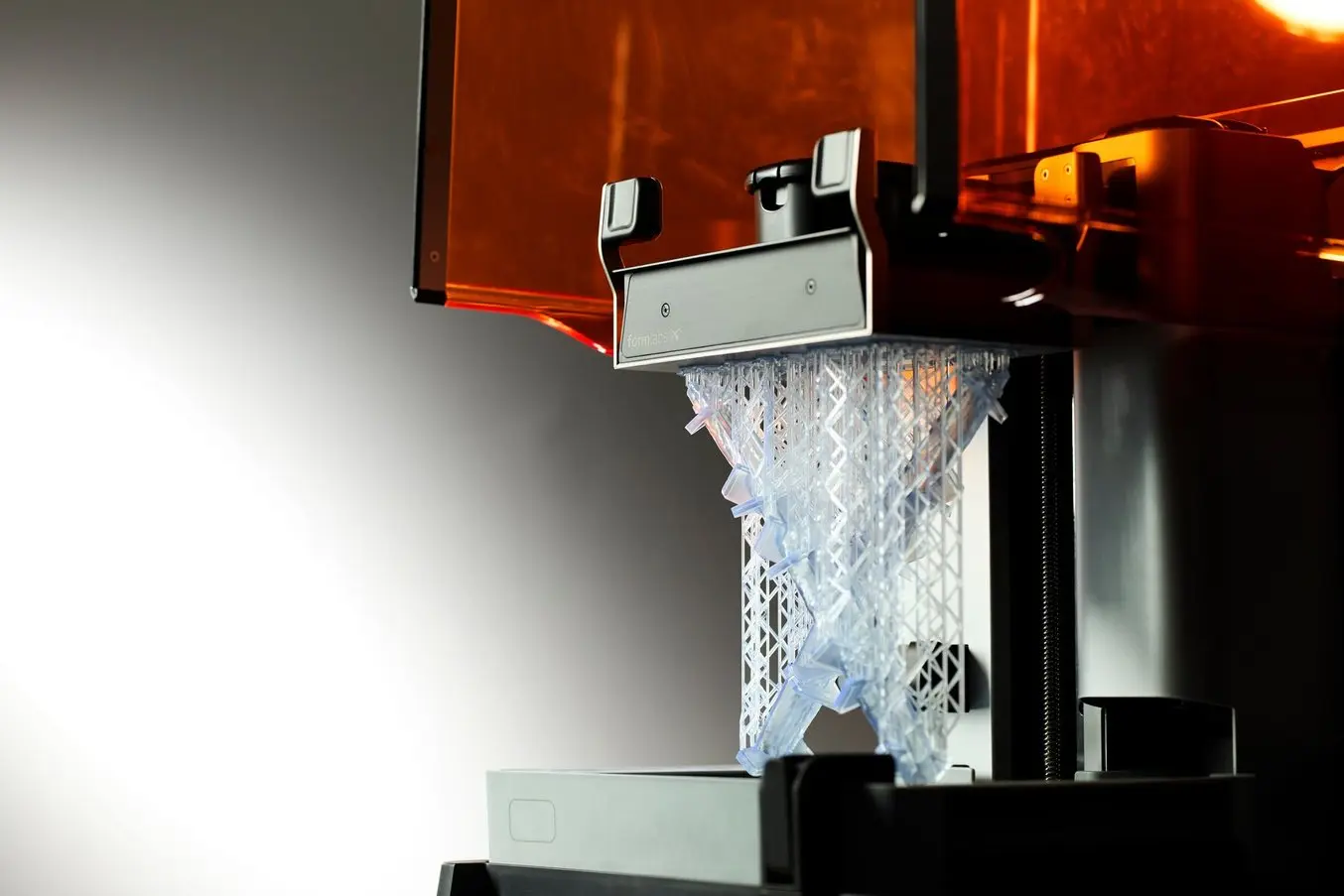

Formlabs' high resolution SLA 3D printers have high Z-axis resolution and a low minimum feature size on the XY plane, allowing them to produce fine details
What makes a 3D printer high resolution? There’s not a one-number answer. Since 3D printers produce parts in 3 dimensions, you will have to consider at least two numbers: the minimum feature size of the XY plane and the Z-axis resolution (layer thickness or layer height). The Z-axis resolution is easily determined and therefore widely reported even though it is less related to print quality and surface finish. The more important XY resolution (minimum feature size) is measured via microscopic imaging and is therefore not always found in spec sheets.
Practically, it means that you should pick a 3D printer that performs well in both categories (in all 3 dimensions).

Introduction to 3D Printing With Desktop Stereolithography (SLA)
Looking for a 3D printer to realize your 3D models in high resolution? Download our white paper to learn how SLA printing works and why it's the most popular 3D printing process for creating models with increadible details.

Dimensional Accuracy Report
Download this report for an internal test that Formlabs created to determine the dimensional accuracy of the Form 3 and Form 3B.
SLA vs. FDM 3D Printing
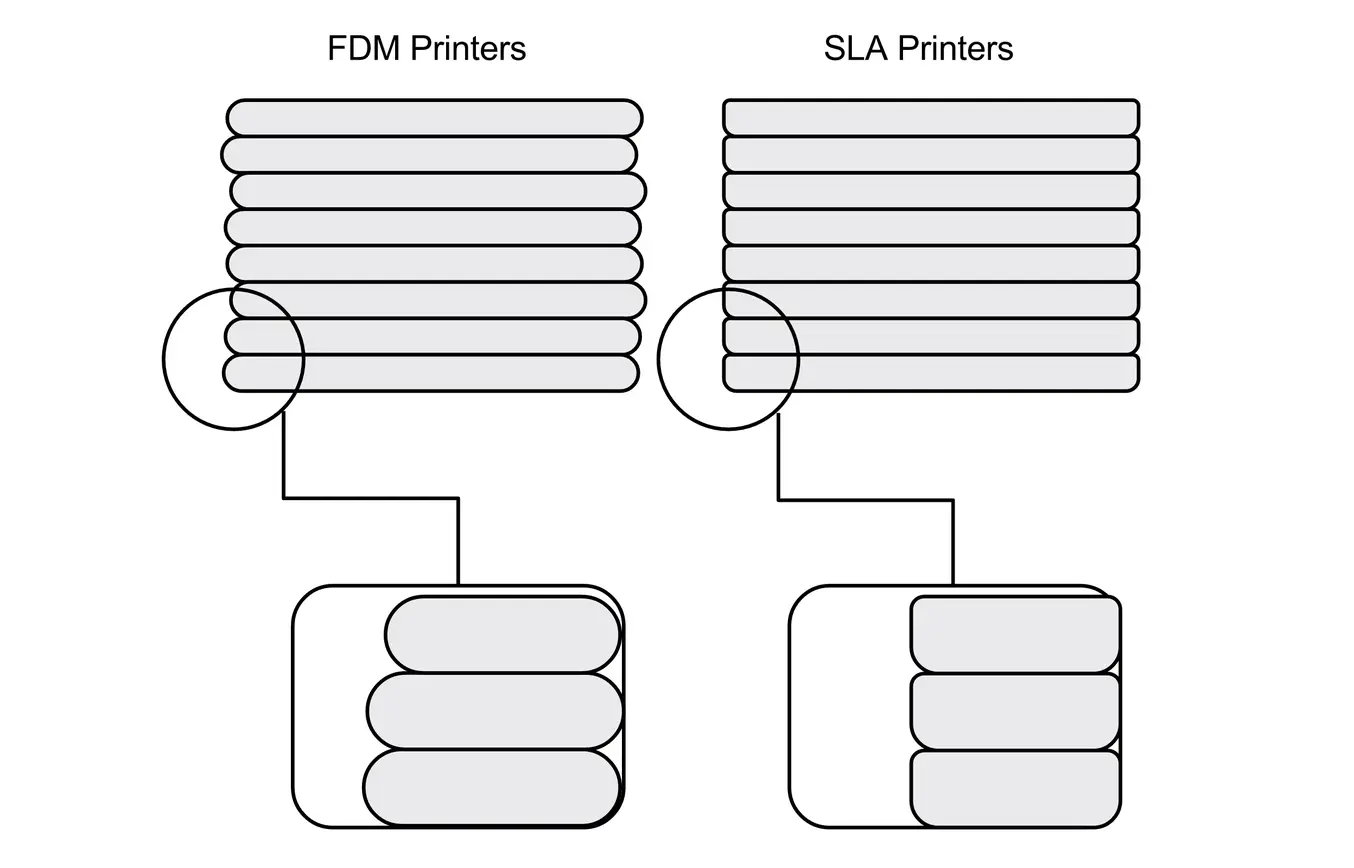
A lot has changed since the first desktop 3D printers became available to the public. Now stereolithography (SLA) 3D printers, like the Form 3+, are competing for the same desktop spots as fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printers. One of the main advantages that resin-based SLA 3D printers hold over their plastic-melting cousins is print quality: SLA 3D printers produce significantly smoother and more detailed prints. While SLA printers can usually also achieve significantly smaller layer thicknesses, the reason for the improved print quality lies in their much higher XY-resolution.
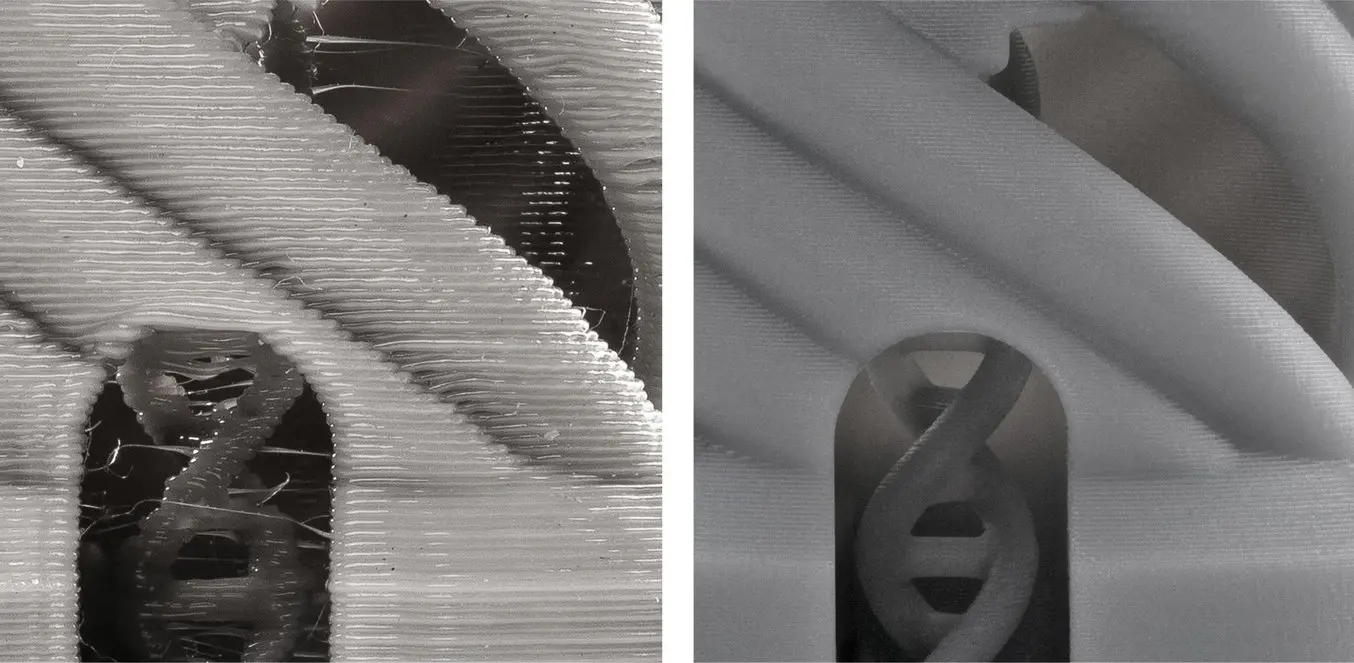

SLA 3D printers (right) offer higher resolution and can produce significantly smoother and more detailed prints than FDM 3D printer (left).
Unlike on FDM 3D printers, minimum feature size in the XY plane on SLA 3D printers is not limited by molten plastic flow dynamics but rather optics and radical polymerization kinetics. While the math is complicated (and outside the scope of this post), it shakes out to this: features on SLA prints can be approximately as small as the diameter of their laser spots. And laser spots can be really small, especially compared to the nozzle size of FDM printers' extruders.
Read our in-depth guide about FDM vs. SLA 3D printers to learn how they compare in terms of print quality, materials, applications, workflow, speed, costs, and more.
Laser SLA vs. DLP 3D Printers
Resin 3D printers like SLA, LFS and DLP technologies offer the highest resolutions of all 3D printing processes available on the desktop. The basic units of the these processes are different shapes, making it difficult to compare the different machines by numerical specifications alone.
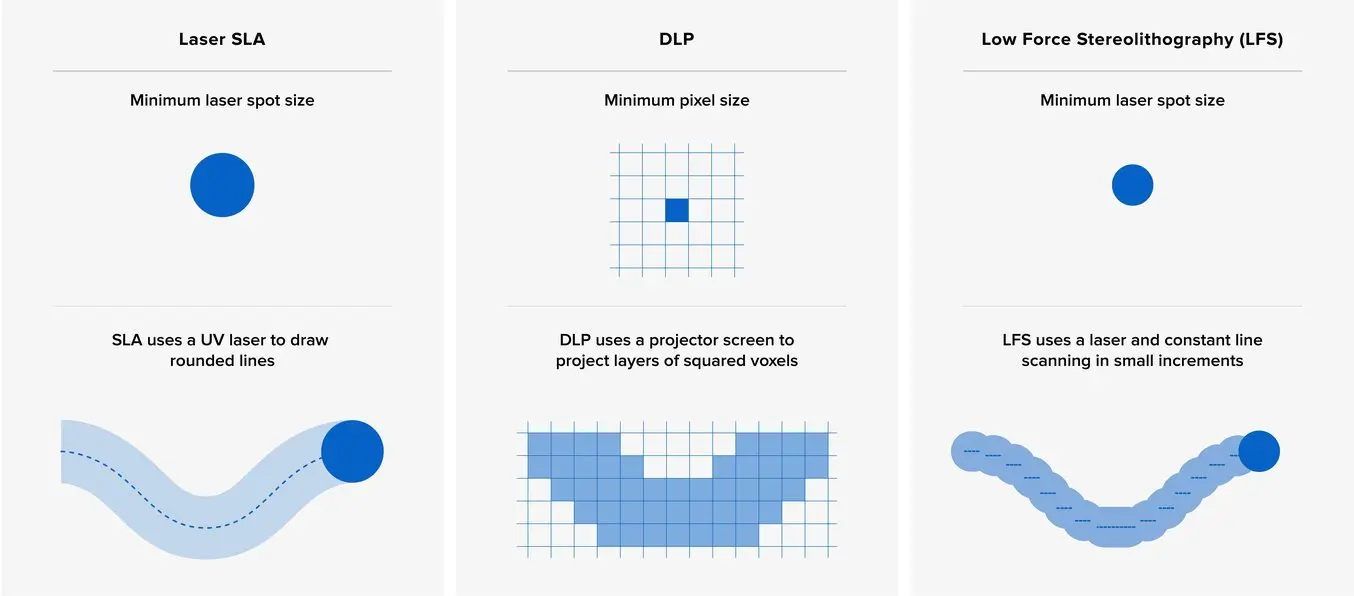
DLP 3D printers have a fixed matrix of pixels relative to the build area, while laser-based SLA and LFS 3D printers can focus the laser beam on any XY coordinate. This means that laser-based machines, given high-quality optics, can more accurately reproduce the surface of a part even if the laser spot size is larger than the DLP pixel size.
Whichever resin 3D printing process you choose, however, professional resin 3D printers should be able to capture the finest details of your creations, from photorealistic models to intricate jewelry.
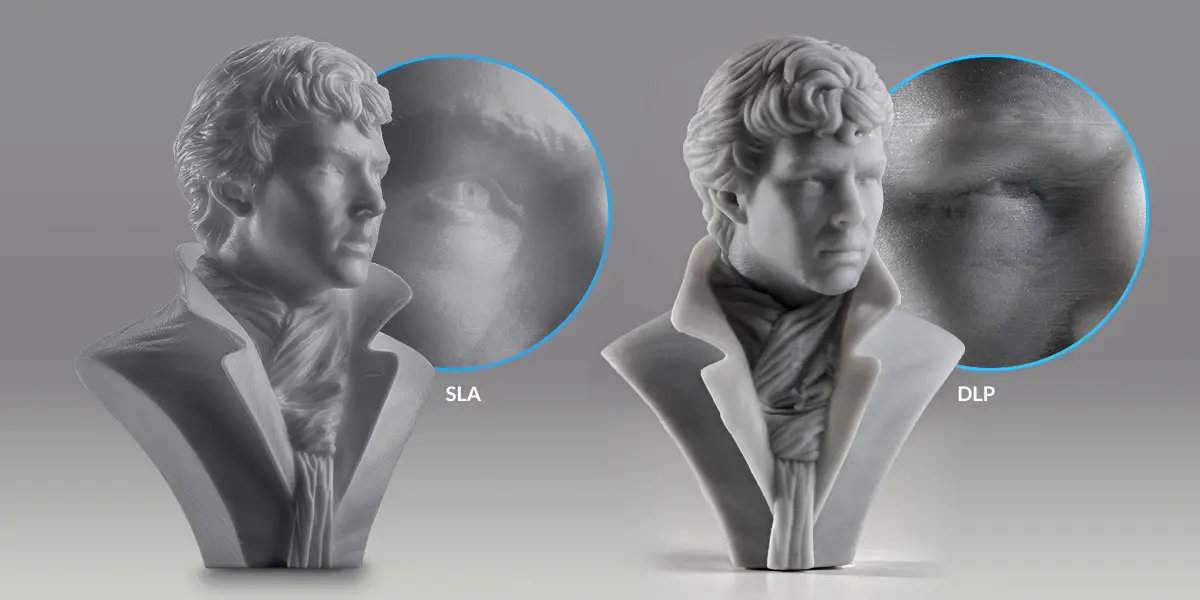

In SLA and LFS 3D printing (left), layer lines are close to invisible. As a result, surface roughness is reduced, which ultimately leads to smooth surfaces, and for clear materials, more translucent parts. DLP 3D printers render images using rectangular voxels, which causes an effect of vertical voxel lines (right).
Learn more about the differences between SLA and DLP 3D printers and see how they compare in terms of resolution, accuracy, precision, build volume, surface finish, speed, and workflow.
Understanding XY Resolution
In the world of 3D printing, no factor influences print quality more than XY resolution. Often discussed but seldom understood, the definition of XY resolution (also called horizontal resolution) varies by 3D printing technology:
- SLA and LFS 3D printers: a combination of the laser’s spot size and the increments by which the laser beam can be controlled
- DLP 3D printers: the pixel size, the smallest feature the projector can reproduce within a single layer
- FDM 3D printers: the smallest movement the extruder can make within a single layer
As a rule of thumb, the lower the number, the better the details. Yet this number is not always included in spec sheets, and when it is, the published value is not always accurate. To truly know a printer’s XY resolution, it’s important to understand the science behind the number.
Practically, how does XY resolution affect your 3D prints? In order to find out, we decided to test the Form 2 SLA 3D printer. The Form 2 has a laser spot size of 140 microns (FWHM), which should allow it to print fine details on the XY plane. We put it to the test to see if this ideal resolution holds true.
Designing a Model to Test 3D Printer Resolution
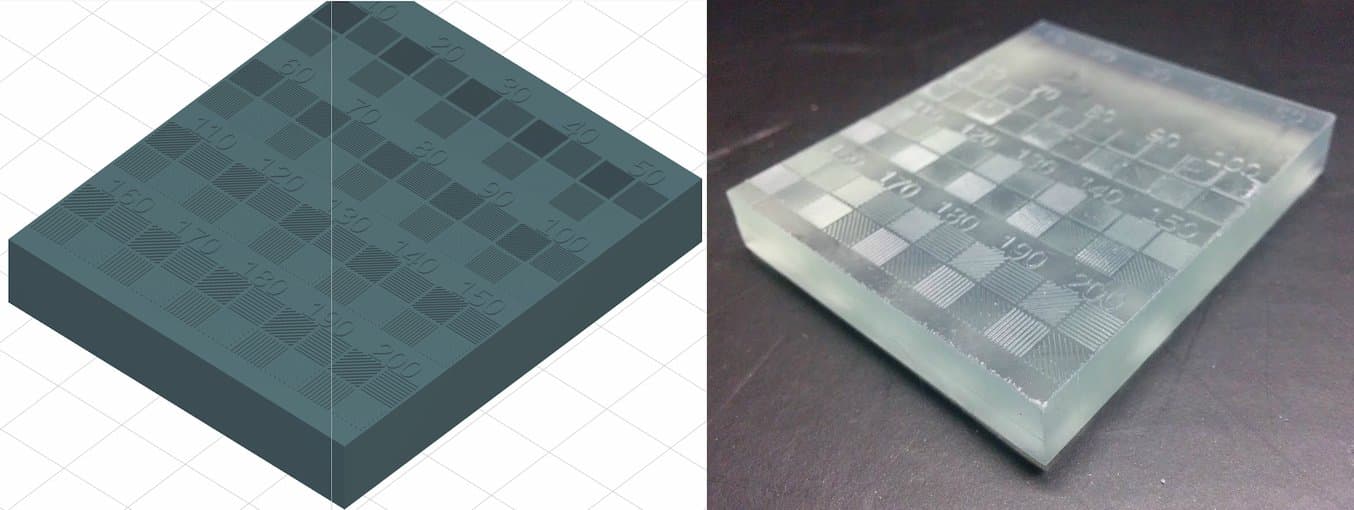
To test the Form 2’s minimum feature size on the XY plane, we designed a model (left) with lines ranging from 10 to 200 microns and printed it in Clear Resin (right).
First, we designed and printed a model to test the minimum feature size on the XY plane. The model is a rectangular block with lines of varying widths in horizontal, vertical, and diagonal directions to avoid directional bias. The line widths range from 10 to 200 microns in 10 micron steps and are 200 microns tall, which equates to two layers when printed at 100-micron Z resolution. The model was printed in Clear Resin, washed twice in an IPA bath, and post-cured for 30 minutes.
Analyzing the Model
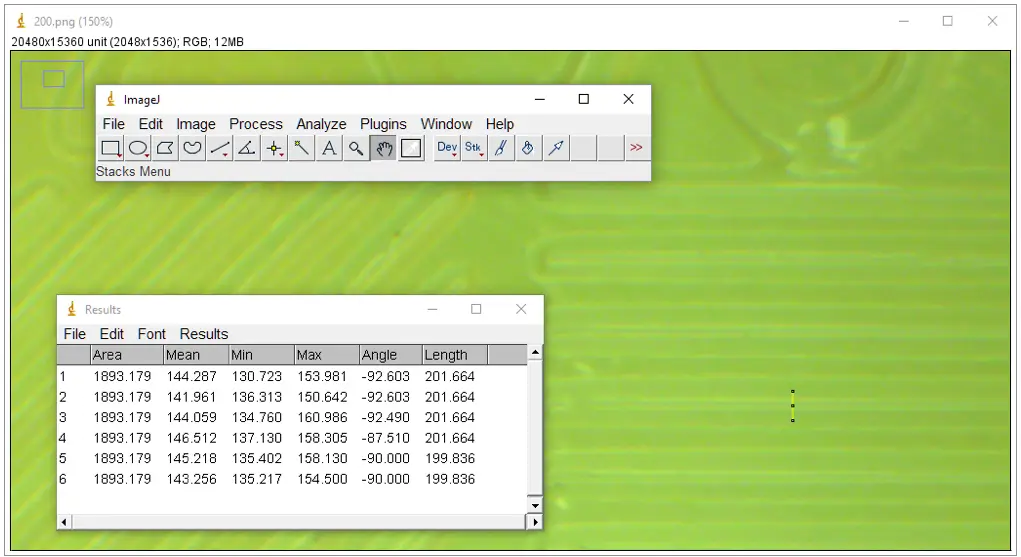
The model was photographed and tinted green to improve visibility. On the right side of the window, the vertical yellow line with black points measures the width of a photographed line.
After post-curing, we put the model under a microscope and took high-resolution photos for analysis. Using ImageJ, the NIH’s free image analysis software, we first scaled the pixels of the images and then measured the actual widths of the lines printed. We collected over 50 data points per line width to eliminate measuring errors and variability. In total, we printed and analyzed three models on two different printers.
Understanding the Results
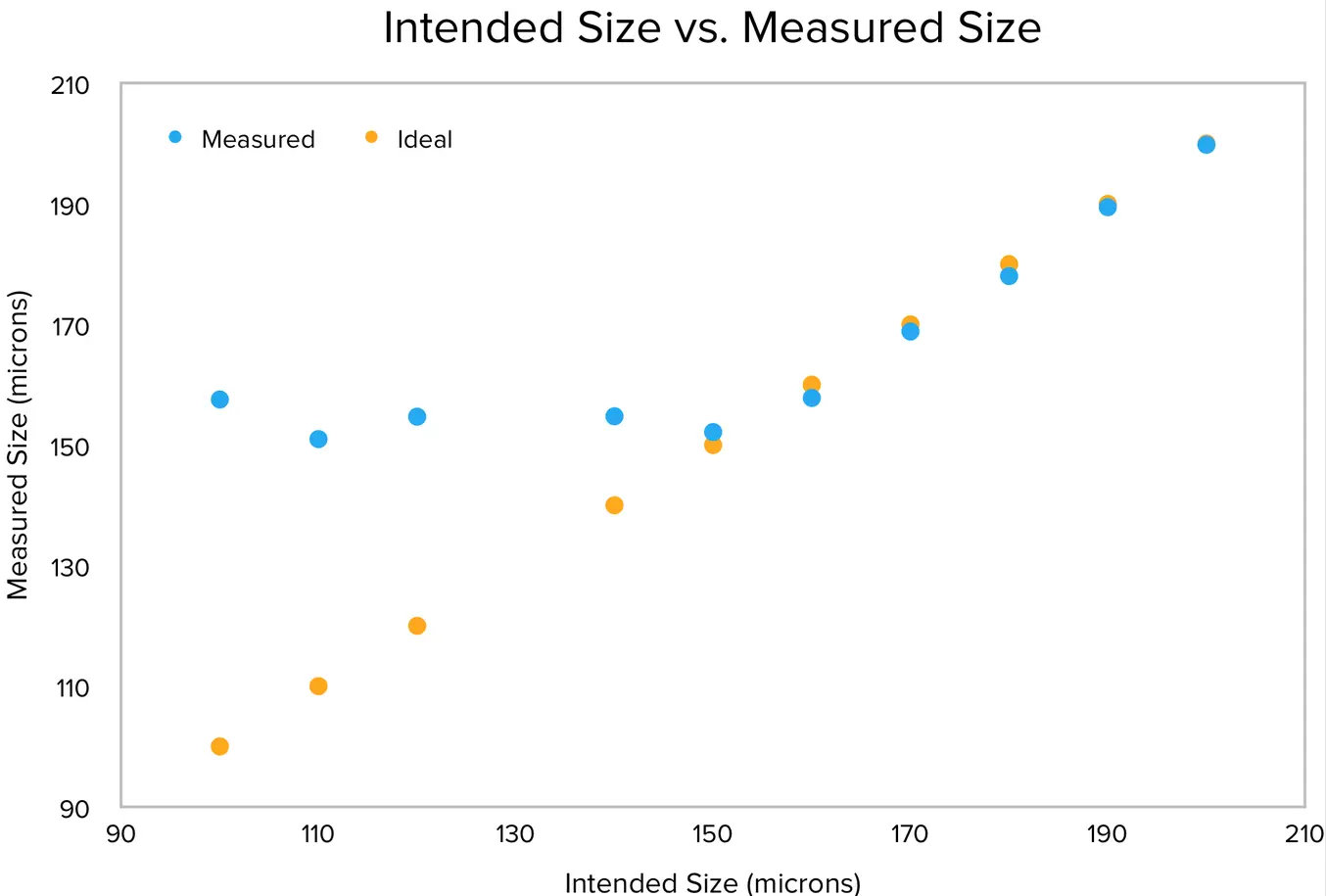
The results indicate that the Form 2 has the same ideal and actual XY resolution for features that are 150 microns and larger.
As the print’s line width decreases from 200 to 150 microns, the ideal values are within the 95% confidence interval of the measured value. As the intended line widths get smaller than 150 microns, the measured interval starts to deviate significantly from the ideal. This means that the printer can reliably produce XY features as small as 150 microns, about the size of a human hair.
The Form 2’s minimum feature size on the XY plane is about 150 microns—only 10 microns larger than its 140-micron laser. The minimum feature size can never be smaller than the laser spot size, and there are many factors that affect this value: laser refraction, microscopic contaminants, resin chemistry, and much more. Considering the printer’s entire ecosystem, a 10-micron difference is nominal. Not every 3D printer’s published resolution holds true, so it’s a good idea to do plenty of research before choosing the one that's right for your project.
If your work calls for prints with intricate details, look for a printer with an XY resolution that’s backed by measurable data, not just a number.
Understanding Z Resolution
When you read 3D printer spec sheets, you’ll see one value show up more than any else: Z resolution. Also known as layer thickness or layer height, the vertical resolution was the first major numerical differentiation between early 3D printers. Early machines struggled to break the 1 mm barrier, but now layer thicknesses on FDM 3D printers can be sub-0.1 mm thin, while LFS and SLA 3D printers are even more precise.
Formlabs 3D printers support layer thicknesses between 25 to 300 microns, depending on the material. This selection of layer heights gives you the ideal balance of speed and resolution. The main question is: what is the best layer thickness for your print?
Are Smaller Layer Thicknesses Always Better?
High resolution 3D printing comes with a tradeoff. Thinner layers mean more repetitions, which in turn means longer times: printing at 25 microns vs. 100 usually increases the print time four-fold. More repetitions also mean more opportunities for something to go wrong. For example, even at a 99.99% success rate per layer, quadrupling the resolution lowers the chance of print success from 90% to 67% if one assumes that a failed layer causes total print failure.
Lower layer thickness equals more time, artifacts, and errors.
Does higher resolution (thinner layers) result in better prints? Not always—it depends on the model to be printed and the 3D printer’s XY resolution. In general, thinner layers equals more time, artifacts, and errors. In some cases, printing models at lower resolutions (i.e. thicker layers) can actually result in higher-quality prints.
When Thinner Layers Don’t Help
Thinner layers are typically associated with smoother transitions on diagonals, which leads many users to generalize and push Z resolution to the limits. But what if the model consists mostly of vertical and horizontal edges, with 90-degree angles and few diagonals? In those cases, additional layers don’t improve the quality of the model.
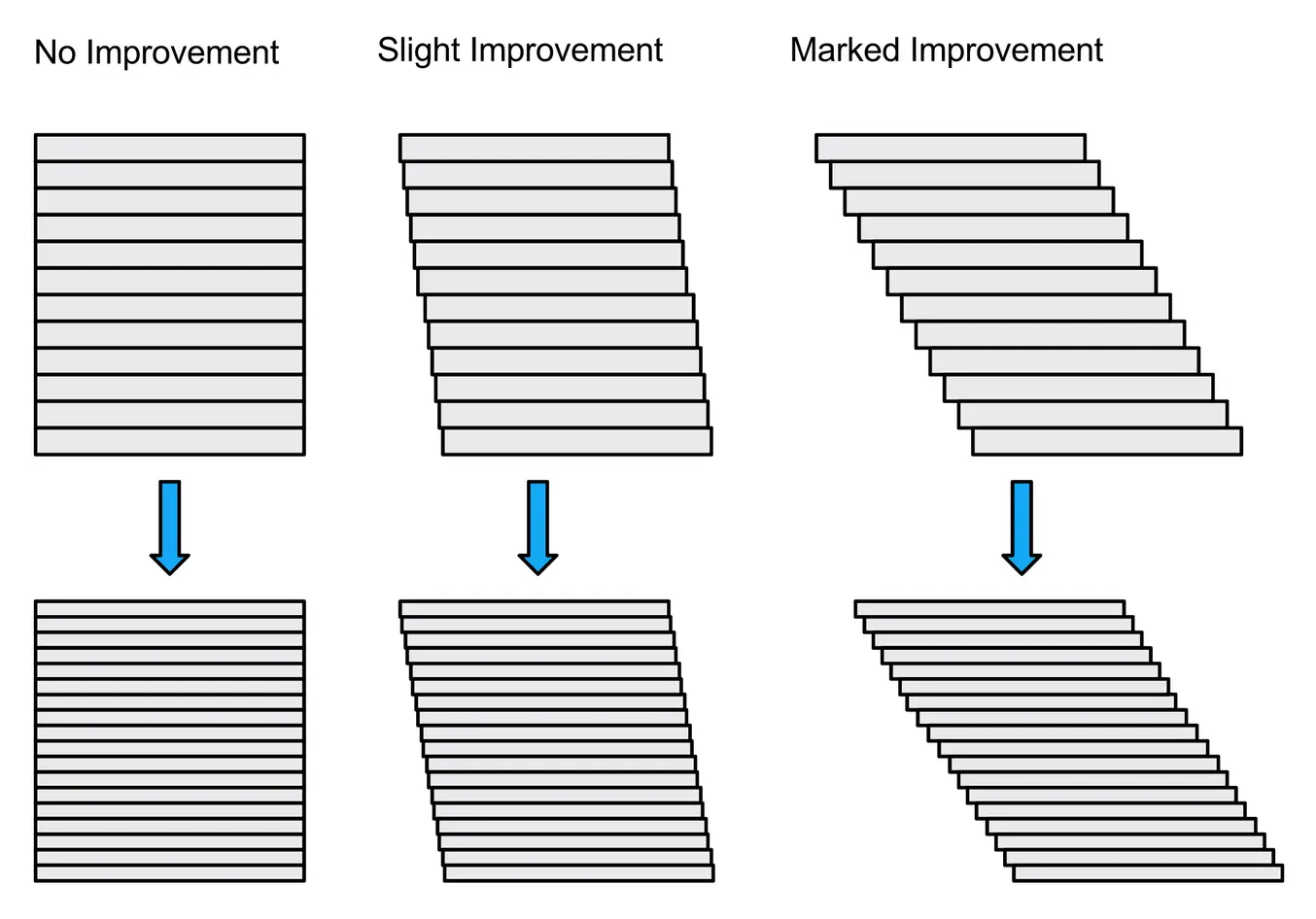
The issue is compounded if the XY resolution of the printer in question is not perfect and “colors outside the lines” when drawing the outside edges. More layers means more mismatched ridges on the surface. While the Z resolution is higher, the model will look like it is significantly lower quality in this case.
When to Choose Higher Z Resolution
That being said, there are times when you want higher resolution. Given a printer with good XY resolution and a model with intricate features and many diagonal edges, dialing down the thickness of the layers will yield a much better model. In addition, if that model is short (200 or fewer layers) upping the Z-axis resolution can really improve the quality.
Certain designs benefit from a higher Z resolution: organic forms, rounded arches, small embossings, and intricate engravings.
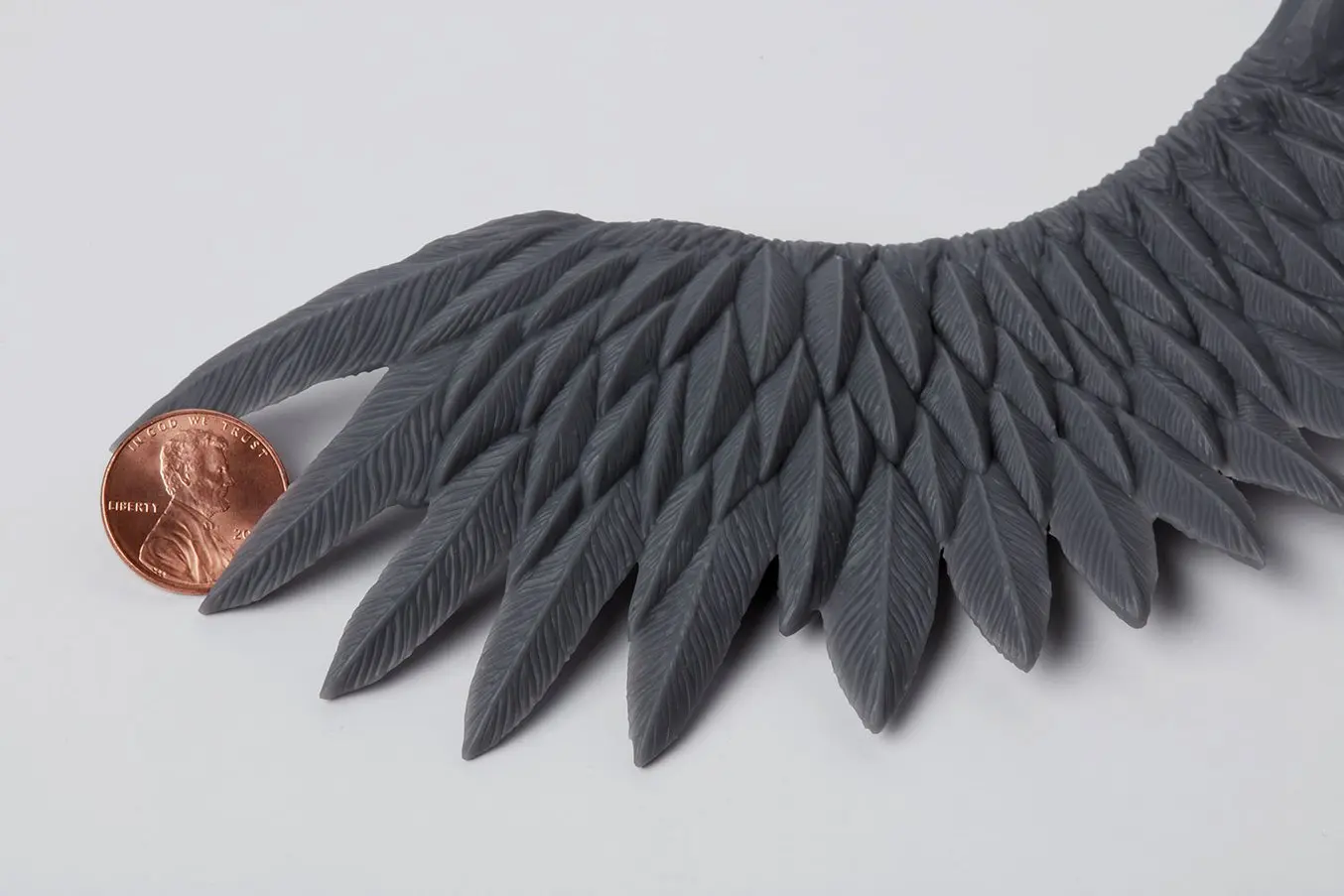

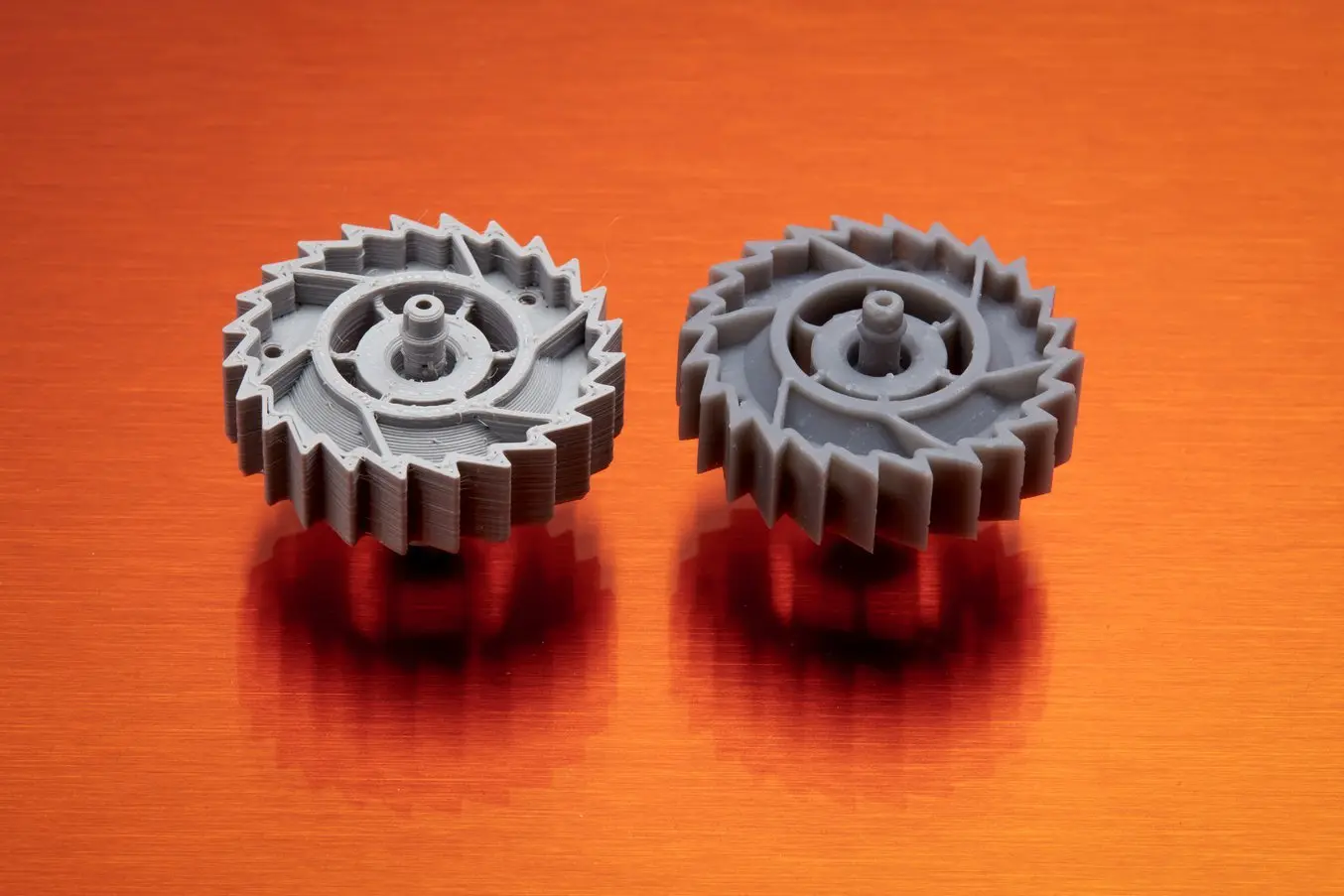
Intricate models with elaborate details call for a higher Z resolution. SLA 3D printed parts have sharp edges, sleek surfaces, and minimal visible layer lines. This example part was printed on the Formlabs Form 3 desktop SLA 3D printer.
As a general guideline, err on the side of thicker layers and only bump up the Z resolution when completely necessary. With the right printer and a certain type of model, higher Z resolution will capture the intricate details of your design.

Draft Resin, the fastest 3D printing resin available for a Formlabs SLA printers, prints at 200 microns and 100 microns, while retaining the a smooth surface finish.
In PreForm, Formlabs provides users with the choice of different layer thicknesses. Depending on the material and the requirements of the application, parts can be printed in the following layer heights: 200, 160, 100, 50, and 25 microns.
Get Started With High Resolution 3D Printing

The desktop Form 4 and the large format Form 4L SLA printers are ideal for high resolution 3D printing.
After learning about 3D printing resolution and sorting out the differences in technology and outcomes, we hope it’s much easier to select 3D printer that best matches your workflow and output needs.
To explore the next generation of SLA 3D printing, learn more about the Form 4 and Form 4L 3D printers.
Curious to see the what high resolution 3D printing looks like firsthand? Order a sample part shipped to your office.