Guide to 3D Printing
Learn how 3D printers work, explore the different types of 3D printers, materials, and explore applications of 3D printing.

What is 3D Printing?
3D printing or additive manufacturing (AM) technologies create three-dimensional parts from computer-aided design (CAD) models by successively adding material layer by layer until physical part is created.
While 3D printing technologies have been around since the 1980s, recent advances in machinery, materials, and software have made 3D printing accessible to a wider range of businesses, enabling more and more companies to use tools previously limited to a few high-tech industries.
Today, professional, low-cost desktop and benchtop 3D printers accelerate innovation and support businesses in various industries including engineering, manufacturing, dentistry, healthcare, education, entertainment, jewelry, and audiology.
While 3D printing technologies have been around since the 1980s, recent advances in machinery, materials, and software have made 3D printing accessible to a wider range of businesses, enabling more and more companies to use tools previously limited to a few high-tech industries.
Today, low-cost desktop 3D printers are widely used by hobbyists, while professional 3D printers accelerate innovation and support businesses in various industries, including engineering, manufacturing, dentistry, healthcare, education, entertainment, jewelry, and audiology.
How Does 3D Printing Work?
All 3D printing processes start with a CAD model that is sent to software to prepare the design. Depending on the technology, the 3D printer might produce the part layer by layer by solidifying resin or sintering powder. The parts are then removed from the printer and post-processed for the specific application.
1. 設計
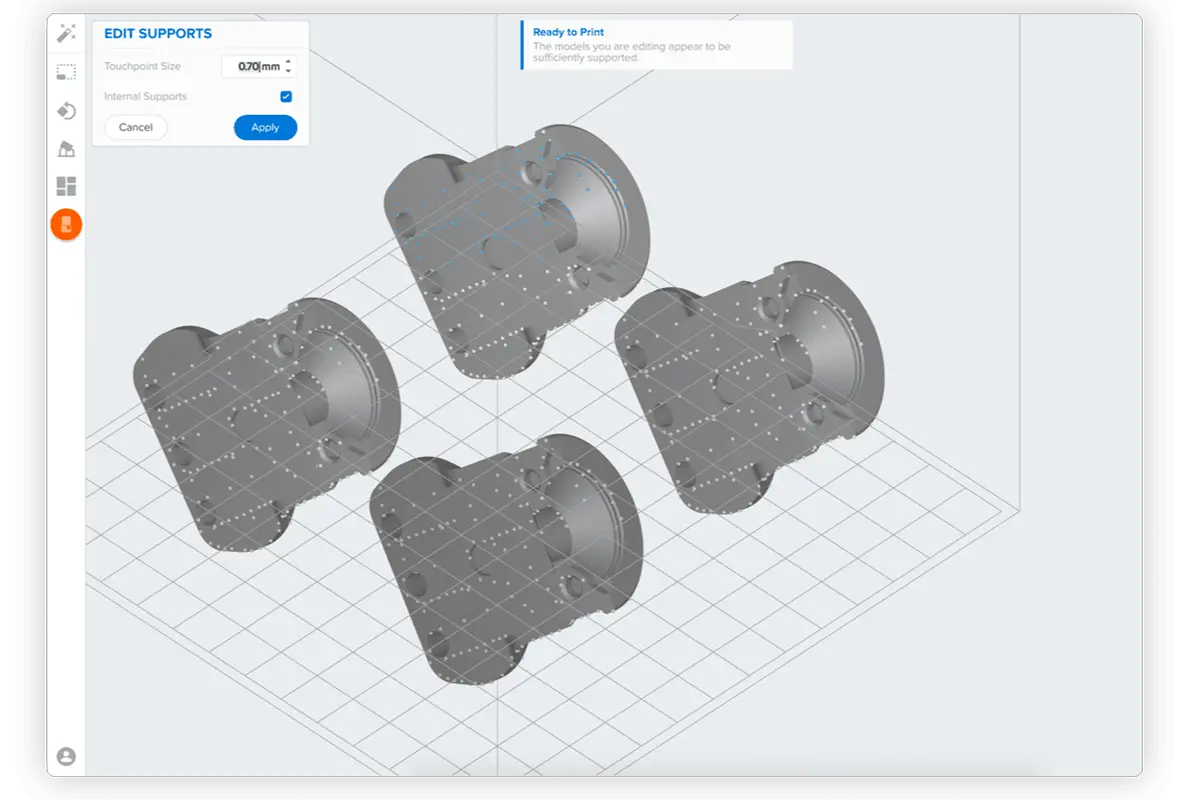
3D printers create parts from three-dimensional models, the mathematical representations of any three-dimensional surface created using computer-aided design (CAD) software or developed from 3D scan data. The design is then exported as an STL or OBJ file readable by print preparation software.
3D printers include software to specify print settings and slice the digital model into layers that represent horizontal cross-sections of the part. Adjustable printing settings include orientation, support structures (if needed), layer height, and material. Once setup is complete, the software sends the instructions to the printer via a wireless or cable connection.
2. 3D Print

3D printers create parts from three-dimensional models, the mathematical representations of any three-dimensional surface created using computer-aided design (CAD) software or developed from 3D scan data. The design is then exported as an STL or OBJ file readable by print preparation software.
3D printers include software to specify print settings and slice the digital model into layers that represent horizontal cross-sections of the part. Adjustable printing settings include orientation, support structures (if needed), layer height, and material. Once setup is complete, the software sends the instructions to the printer via a wireless or cable connection.
3. 後処理

Depending on the technology and the material, the printed parts may require rinsing in isopropyl alcohol (IPA) to remove any uncured resin from their surface, post-curing to stabilize mechanical properties, manual work to remove support structures, or cleaning with compressed air or a media blaster to remove excess powder. Some of these processes can be automated with accessories.
3D printed parts can be used directly or post-processed for specific applications and the required finish by machining, priming, painting, fastening or joining. Often, 3D printing also serves as an intermediate step alongside conventional manufacturing methods, such as positives for investment casting jewelry and dental appliances, or molds for custom parts.
Types of 3D Printers
The three most established types of 3D printers for plastics parts are stereolithography (SLA), selective laser sintering (SLS), and fused deposition modeling (FDM). Formlabs offers two professional 3D printing technologies, SLA and SLS, bringing these powerful and accessible industrial fabrication tools into the creative hands of professionals around the world.
SLA光造形
Stereolithography was the world’s first 3D printing technology, invented in the 1980s, and is still one of the most popular technologies for professionals. SLA 3D printers use a laser to cure liquid resin into hardened plastic in a process called photopolymerization.
SLA resin 3D printers have become vastly popular for their ability to produce high-accuracy, isotropic, and watertight prototypes and parts in a range of advanced materials with fine features and smooth surface finish. SLA resin formulations offer a wide range of optical, mechanical, and thermal properties to match those of standard, engineering, and industrial thermoplastics.
Resin 3D printing a great option for highly detailed prototypes requiring tight tolerances and smooth surfaces, such as molds, patterns, and functional parts. SLA 3D printers are widely used in a range of industries from engineering and product design to manufacturing, dentistry, jewelry, model making, and education.

SLA parts have sharp edges, a smooth surface finish, and minimal visible layer lines.
Resin 3D Printing Benefits
Resin 3D Printing Benefits
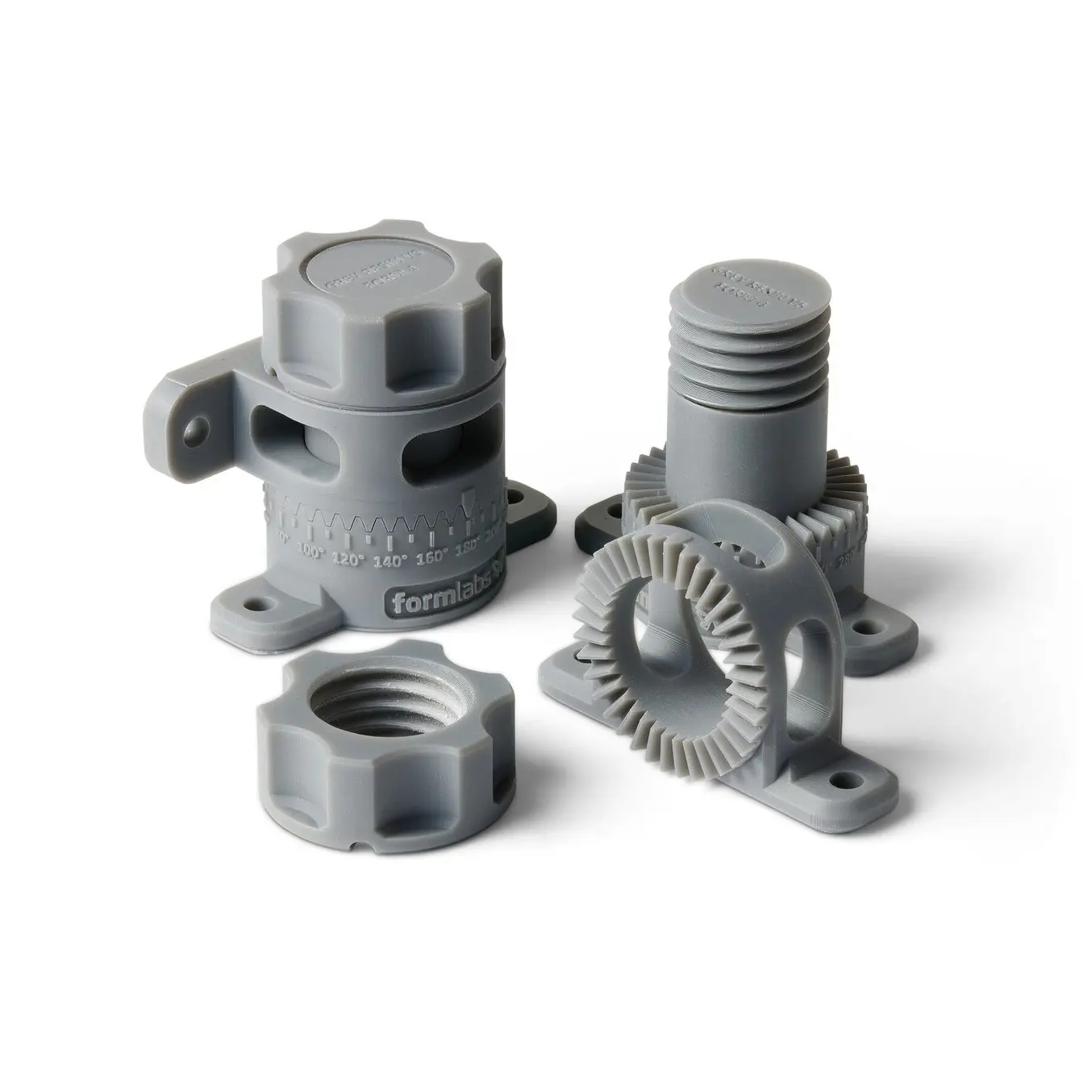

SLA光造形
Stereolithography was the world’s first 3D printing technology, invented in the 1980s, and is still one of the most popular technologies for professionals. SLA 3D printers use a laser to cure liquid resin into hardened plastic in a process called photopolymerization.
SLA resin 3D printers have become vastly popular for their ability to produce high-accuracy, isotropic, and watertight prototypes and parts in a range of advanced materials with fine features and smooth surface finish. SLA resin formulations offer a wide range of optical, mechanical, and thermal properties to match those of standard, engineering, and industrial thermoplastics.
Resin 3D printing a great option for highly detailed prototypes requiring tight tolerances and smooth surfaces, such as molds, patterns, and functional parts. SLA 3D printers are widely used in a range of industries from engineering and product design to manufacturing, dentistry, jewelry, model making, and education.

SLS parts have a slightly rough surface finish, but almost no visible layer lines.
Resin 3D Printing Benefits
Resin 3D Printing Benefits

SLA / DLP / MSLA (Resin Printing)
Selective laser sintering (SLS) 3D printers use a high-power laser to sinter small particles of polymer powder into a solid structure. The unfused powder supports the part during printing and eliminates the need for dedicated support structures. This makes SLS ideal for complex geometries, including interior features, undercuts, thin walls, and negative features. Parts produced with SLS printing have excellent mechanical characteristics, with strength resembling that of injection-molded parts.
The most common material for selective laser sintering is nylon, a popular engineering thermoplastic with excellent mechanical properties. Nylon is lightweight, strong, and flexible, as well as stable against impact, chemicals, heat, UV light, water, and dirt.
The combination of low cost per part, high productivity, and established materials make SLS a popular choice among engineers for functional prototyping, and a cost-effective alternative to injection molding for limited-run or bridge manufacturing.

FDM parts tend to have visible layer lines and might show inaccuracies around complex features.
Resin 3D Printing Benefits
Resin 3D Printing Benefits
SLA / DLP / MSLA (Resin Printing)
Powder bed fusion 3D printing, commonly referred to as powder 3D printing, is the most common additive manufacturing technology for industrial applications, trusted by engineers and manufacturers across different industries for its ability to produce strong, functional parts. The two most popular processes are selective laser sintering (SLS) and multi-jet fusion (MJF) technology.
SLS 3D printers use a high-power laser to sinter small particles of polymer powder into a solid structure. The unfused powder supports the part during printing and eliminates the need for dedicated support structures. This makes SLS ideal for complex geometries, including interior features, undercuts, thin walls, and negative features. Parts produced with SLS 3D printing have excellent mechanical characteristics, with strength resembling that of injection-molded parts.
The most common material for powder 3D printing is nylon, a popular engineering thermoplastic with excellent mechanical properties. Nylon is lightweight, strong, and flexible, as well as stable against impact, chemicals, heat, UV light, water, and dirt. Other popular materials include nylon composites, TPU, and polypropylene (PP).
The combination of low cost per part, high productivity, and established materials makes SLS a popular choice among engineers for functional prototyping, and a cost-effective alternative to injection molding for limited-run or bridge manufacturing.

FDM parts tend to have visible layer lines and might show inaccuracies around complex features.
Resin 3D Printing Benefits
Resin 3D Printing Benefits
バインダージェット
Filament deposition, also known as fused deposition modeling (FDM) and fused filament fabrication (FFF), is the most widely used type of 3D printing at the consumer level. FDM 3D printers work by extruding thermoplastic filaments, such as ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), PLA (Polylactic Acid), through a heated nozzle, melting the material, and depositing it along programmed paths layer by layer on a build platform.
FDM 3D printers are well-suited for basic proof-of-concept models, as well as quick and low-cost prototyping of simple parts, such as parts that might typically be machined. However, FDM has the lowest resolution and accuracy when compared to SLA or SLS and is not the best option for printing complex designs or parts with intricate features. Higher-quality finishes may be obtained through chemical and mechanical polishing processes. Industrial FDM 3D printers use soluble supports to mitigate some of these issues and offer a wider range of engineering thermoplastics, but they also come at a steep price.

FDM parts tend to have visible layer lines and might show inaccuracies around complex features.
Resin 3D Printing Benefits
Resin 3D Printing Applications
バインダージェット
Material jetting, often called PolyJet or MultiJet Printing (MJP), part of the broader family of inkjet-based additive manufacturing, emerged in the late 1990s and early 2000s and remains popular among industrial designers, medical modelers, and engineering teams for appearance models and fit/ergonomic studies. It’s used by both service bureaus and in-house prototyping labs because it combines exceptional surface finish with true multi-material and full-color capability in a single print.
Material jetting printers deposit tiny droplets of liquid photopolymer through arrays of inkjet nozzles and cure them instantly with UV light. Some printers can jet multiple materials simultaneously — rigid, elastomeric, transparent, and colored photopolymers — making it possible to vary properties voxel by voxel across the part. This enables sharp details, smooth surfaces, and multi-material gradients — useful for showing soft overmolds, clear windows, or full-color labels.
Material jetting (PolyJet) is a great choice for highly realistic prototypes with tight tolerances and a production-ready look and feel. However, material jetting is only compatible with relatively low-viscosity photopolymers, so the printed parts can be brittle, creep under load, and degrade or yellow when exposed to prolonged UV or heat. Mechanical strength and long-term dimensional stability generally trail both SLS/MJF printers and resin 3D printing processes like SLA, DLP, or MSLA. Machines and resins are also expensive and often proprietary; and support removal (typically a gel that’s water- or blast-washed away) adds labor and can mark delicate features.

FDM parts tend to have visible layer lines and might show inaccuracies around complex features.
Powder 3D Printing Benefits
Powder 3D Printing Applications
正しい3Dプリント方式の選定方法は?
Having trouble finding the best 3D printing process for your needs? In this video guide, we compare FDM, SLA, and SLS technologies, the most popular types of 3D printers for plastic parts, across the most important buying considerations.
品質
Different 3D printing technologies are suited to different applications, and one of the most important determining factors is the availability and performance of materials.
材料
Different 3D printing technologies are suited to different applications, and one of the most important determining factors is the availability and performance of materials.
使いやすさ
Different 3D printing technologies are suited to different applications, and one of the most important determining factors is the availability and performance of materials.
速度
Different 3D printing technologies are suited to different applications, and one of the most important determining factors is the availability and performance of materials.
コスト
Different 3D printing technologies are suited to different applications, and one of the most important determining factors is the availability and performance of materials.
The Benefits of 3D Printing
As additive manufacturing processes build objects by adding material layer by layer, they offer a unique set of advantages over traditional subtractive and formative manufacturing processes.
速度
With traditional manufacturing processes, it can take weeks or months to receive a part. 3D printing turns CAD models into physical parts within a few hours, producing parts and assemblies from one-off concept models to functional prototypes and even small production runs for testing. This allows designers and engineers to develop ideas faster, and helps companies to bring products more quickly to the market.
Engineers at the AMRC turned to 3D printing to rapidly produce 500 high-precision drilling caps used in drilling trials for Airbus, cutting the lead time from weeks to only three days.
コスト
With 3D printing, there’s no need for the costly tooling and setup associated with injection molding or machining; the same equipment can be used from prototyping to production to create parts with different geometries. As 3D printing becomes increasingly capable of producing functional end-use parts, it can complement or replace traditional manufacturing methods for a growing range of applications in low- to mid-volumes.
Pankl Racing Systems substituted machined jigs and fixtures with 3D printed parts, decreasing costs by 80-90 percent that resulted in $150,000 in savings.
カスタマイズ性
From shoes to clothes and bicycles, we’re surrounded by products made in limited, uniform sizes as businesses strive to standardize products to make them economical to manufacture. With 3D printing, only the digital design needs to be changed to tailor each product to the customer without additional tooling costs. This transformation first started to gain a foothold in industries where custom fit is essential, such medicine and dentistry, but as 3D printing becomes more affordable, it’s increasingly being used to mass customize consumer products.
Gillette's Razor Maker™ gives consumers the power to create and order customized 3D printed razor handles, with the choice of 48 different designs (and counting), a variety of colors, and the option to add custom text.
設計の自由度
3D printing can create complex shapes and parts, such as overhangs, microchannels, and organic shapes, that would be costly or even impossible to produce with traditional manufacturing methods. This provides the opportunity to consolidate assemblies into less individual parts to reduce weight, alleviate weak joints, and cut down on assembly time, unleashing new possibilities for design and engineering.
Nervous System launched the first-ever 3D printed ceramic jewelry line, consisting of intricate designs that would be impossible to manufacture using any other ceramic technique.
Reduced Risk
Product development is an iterative process that requires multiple rounds of testing, evaluation, and refinement. Finding and fixing design flaws early can help companies avoid costly revisions and tooling changes down the road. With 3D printing, engineers can thoroughly test prototypes that look and perform like final products, reducing the risks of usability and manufacturability issues before moving into production.
The developers of Plaato, an optically clear airlock for homebrewing, 3D printed 1,000 prototypes to fine tune their design before investing in expensive tooling.
Applications and Uses of 3D Printing
3D printing accelerates innovation and supports businesses across a wide range of industries, including engineering, manufacturing, dentistry, healthcare, education, entertainment, jewelry, audiology, and more.

エンジニアリングとプロダクトデザイン
Rapid prototyping with 3D printing empowers engineers and product designers to turn ideas into realistic proofs of concept, advance these concepts to high-fidelity prototypes that look and work like final products, and guide products through a series of validation stages toward mass production.
Applications:
- Rapid prototyping
- Communication models
- Manufacturing validation

製造
Manufacturers automate production processes and streamline workflows by prototyping tooling and directly 3D printing custom tools, molds, and manufacturing aids at far lower costs and lead times than with traditional manufacturing. This reduces manufacturing costs and defects, increases quality, speeds up assembly, and maximizes labor effectiveness.
Applications:
- Rapid tooling
- Manufacturing aids (jig and fixtures)
- Molding (injection molding, thermoforming, silicone molding, overmolding)
- Metal casting
- Low volume production
- Mass customization

歯科
Digital dentistry reduces the risks and uncertainties introduced by human factors, providing higher consistency, accuracy, and precision at every stage of the workflow to improve patient care. 3D printers can produce a range of high-quality custom products and appliances at low unit costs with superior fit and repeatable results.
Applications:
- Crown and bridge models
- Clear aligner and Hawley retainer models
- Surgical guides
- Splints and occlusal guides
- Patterns for casting and pressing
- Dentures
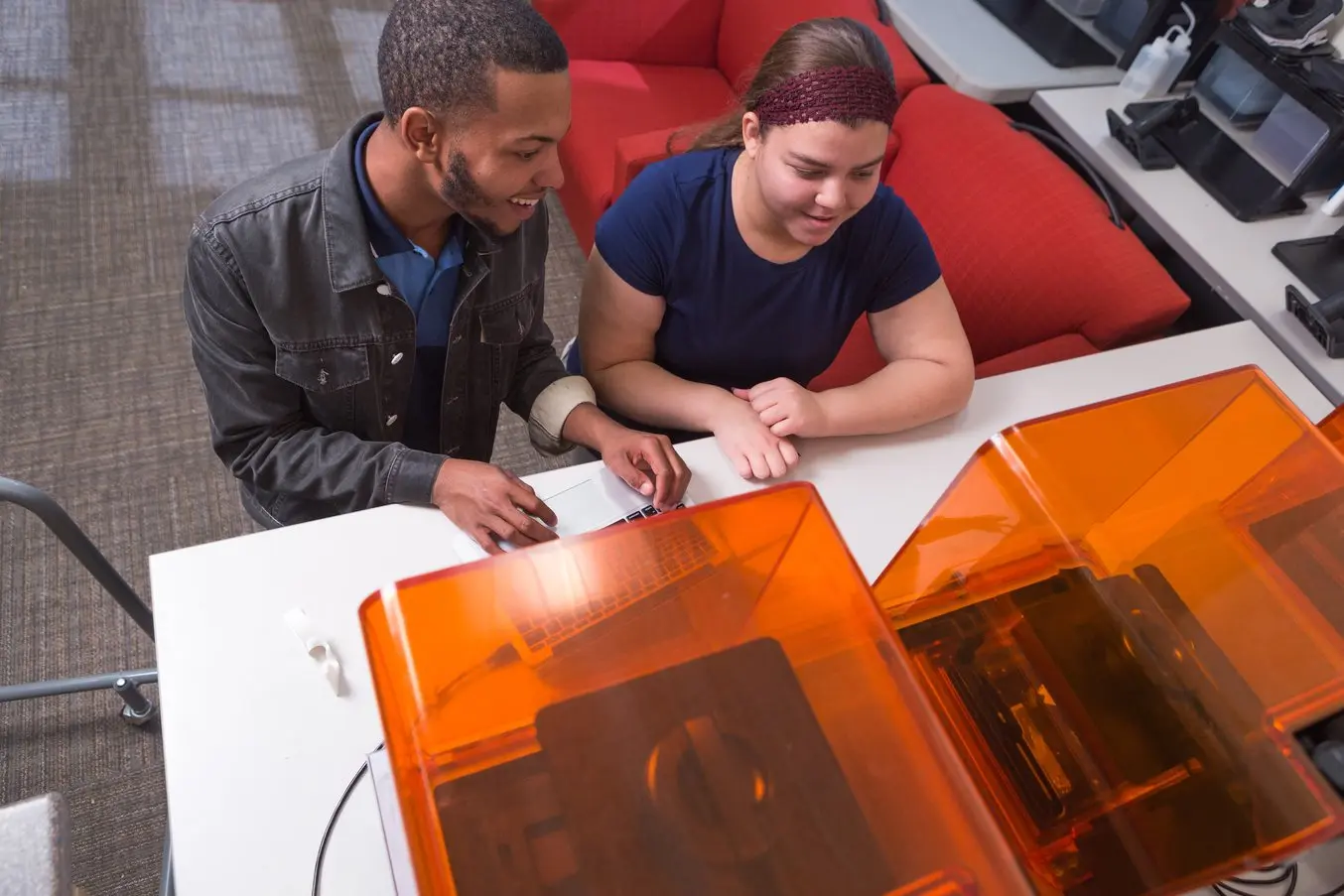

教育
3D printers are multifunctional tools for immersive learning and advanced research. They can encourage creativity and expose students to professional-level technology while supporting STEAM curricula across science, engineering, art, and design.
Applications:
- Models for STEAM curricula
- Fab labs and makerspaces
- Custom research setups
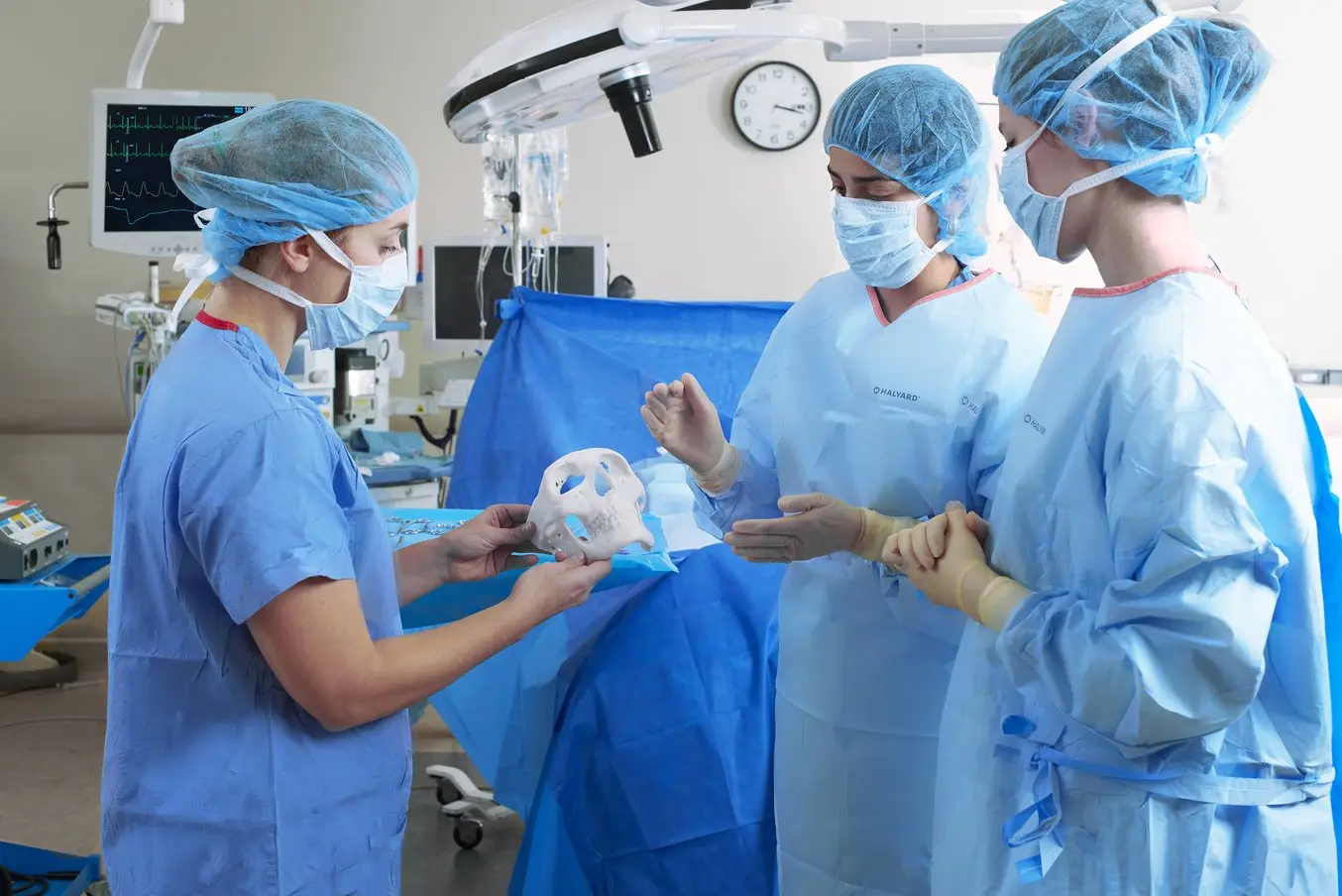
ヘルスケア
Affordable, professional-grade desktop 3D printing helps doctors deliver treatments and devices customized to better serve each unique individual, opening the door to high-impact medical applications while saving organizations significant time and costs from the lab to the operating room.
Applications:
- Anatomical models for surgical planning
- Medical devices and surgical instruments
- Insoles and orthotics
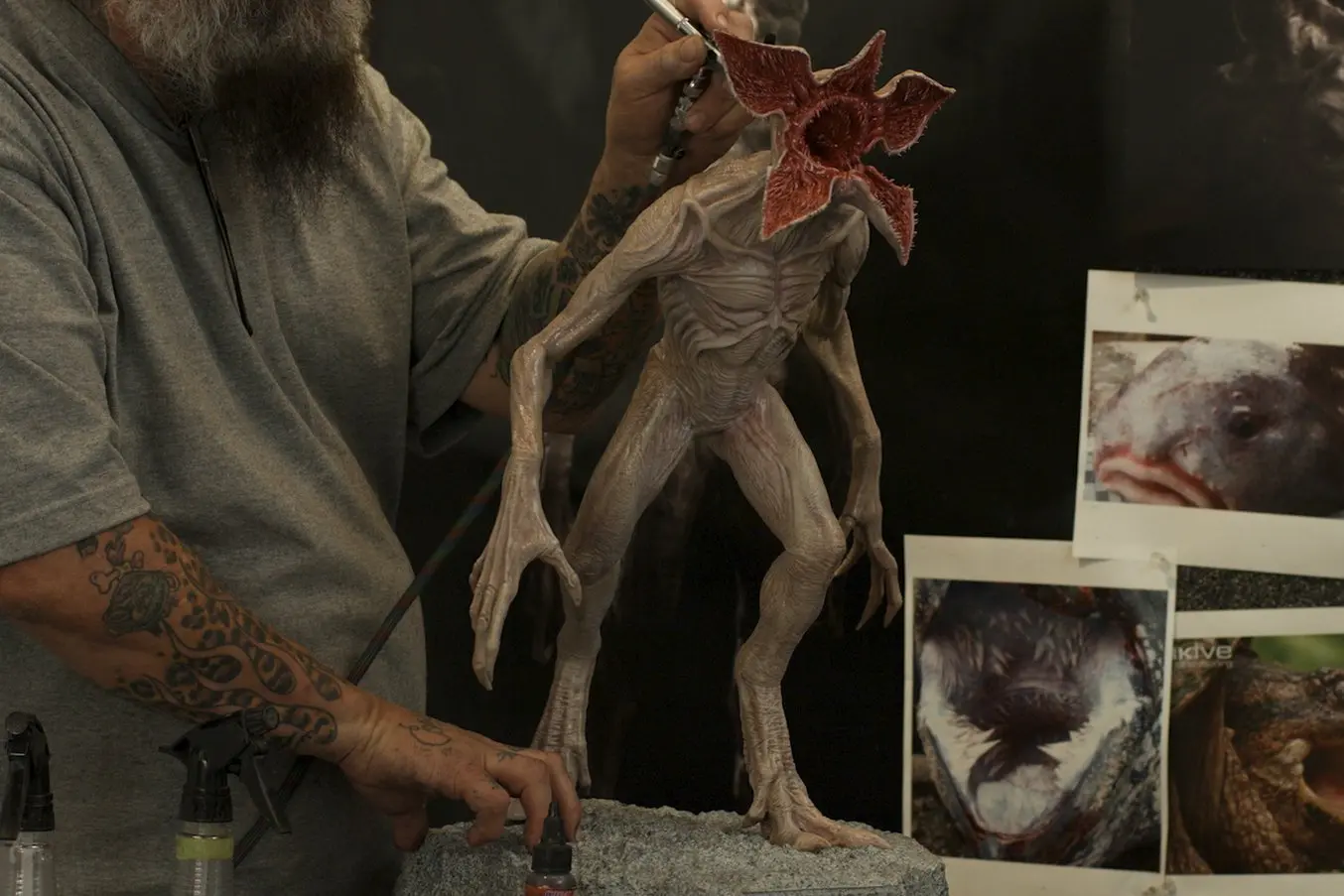

エンターテインメント
High definition physical models are widely used in sculpting, character modeling, and prop making. 3D printed parts have starred in stop-motion films, video games, bespoke costumes, and even special effects for blockbuster movies.
Applications:
- Hyper-realistic sculptures
- Character models
- Props
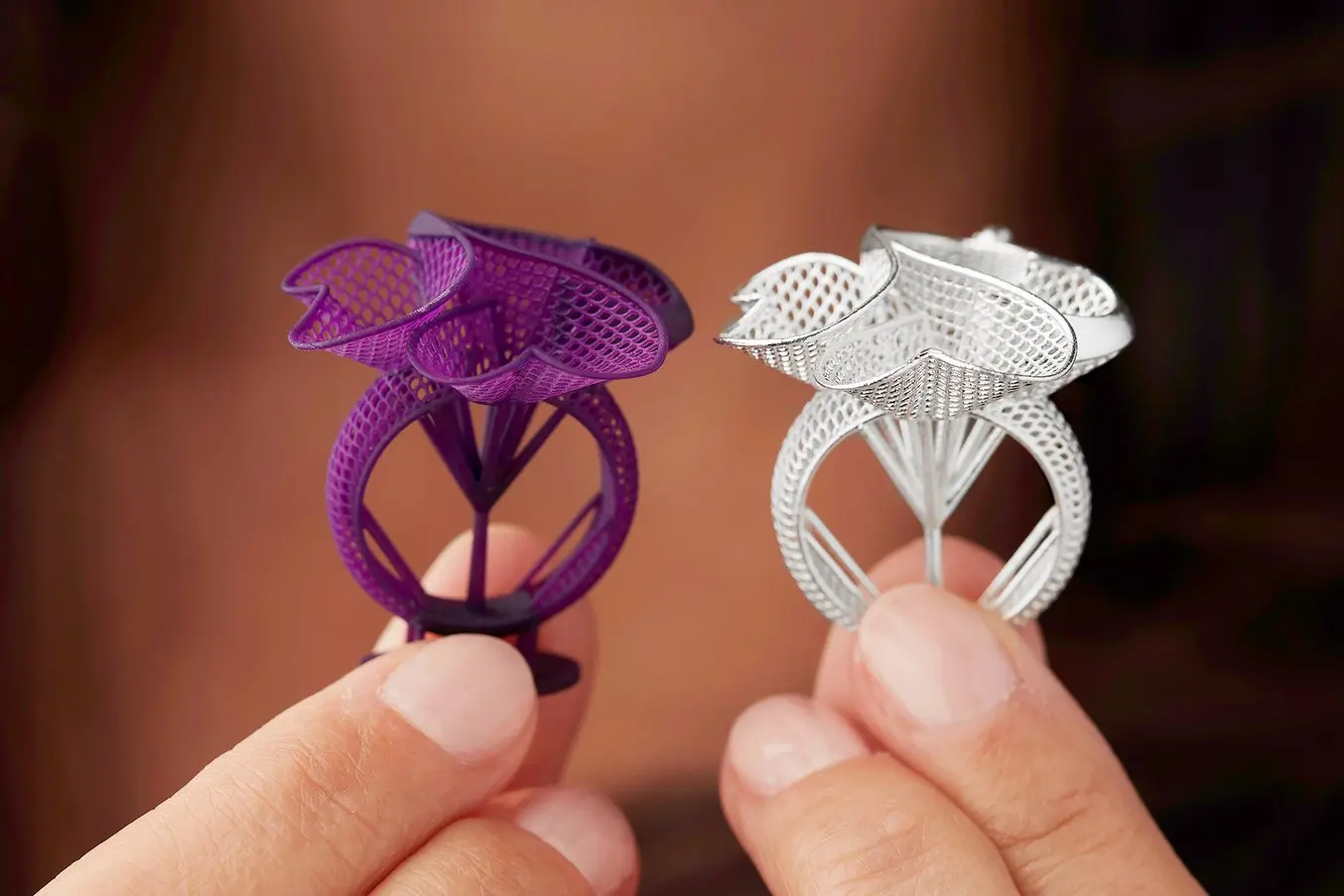

ジュエリー
Jewelry professionals use CAD and 3D printing to rapidly prototype designs, fit clients, and produce large batches of ready-to-cast pieces. Digital tools allow for the creation of consistent, sharply detailed pieces without the tediousness and variability of wax carving.
Applications:
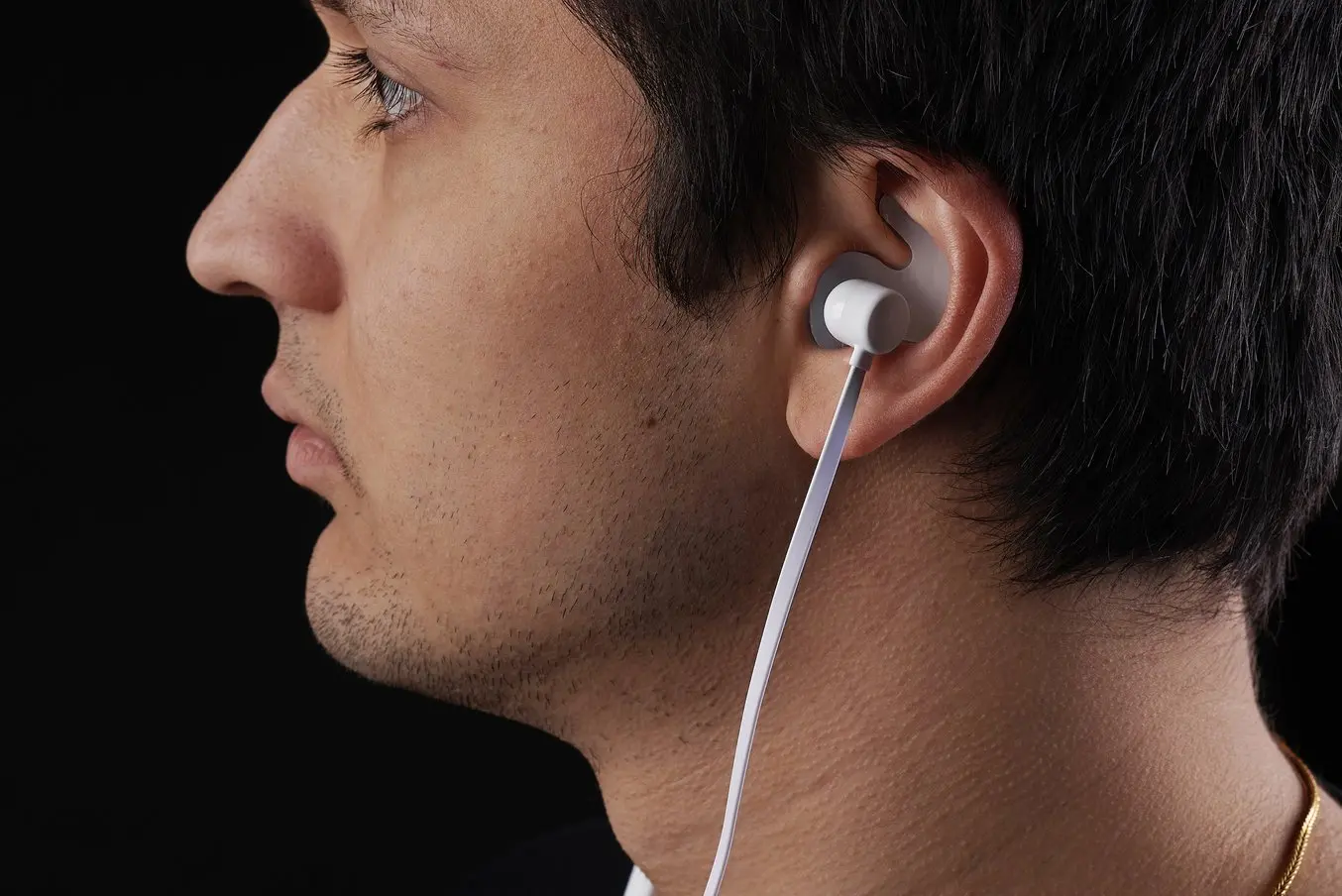

オーディオ
Hearing specialists and ear mold labs use digital workflows and 3D printing to manufacture higher quality custom ear products more consistently, and at higher volumes for applications like behind-the-ear hearing aids, hearing protection, and custom earplugs and earbuds.
Applications:
- Soft silicone ear molds
- Custom earbuds
Materials for 3D Printing
3D printing empowers you to prototype and manufacture parts for a wide range of applications quickly and cost-effectively. But choosing the right 3D printing process is just one side of the coin. Ultimately, it'll be largely up to the materials to enable you to create parts with the desired mechanical properties, functional characteristics, or looks.
Performance from parts made using different 3D printing processes can often be difficult to directly compare because the technologies don’t use the same materials or form parts in the same process. However, there are analogous materials across all technologies, so achieving the same material properties (or very close) can be straightforward even when changing technologies.
| FDM/FFF Filaments | SLA/DLP/MSLA Resins | SLS/MJF Powders | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 一般的な使用 | PLA | スタンダードレジン(マット、クリア、豊富な色彩) | Nylon 12パウダー |
| 丈夫なエンジニアリング材料 | ABS、ナイロン、PETG | Toughレジン、Durableレジン | Nylon 12、Nylon 11、PP |
| 剛性のあるエンジニアリング材料 | PEEK、ULTEM 複合材(ガラス充填または炭素繊維強化材料) | 高剛性・高強度・硬質レジン(ガラス充填) | ナイロン複合材(ガラス充填または炭素繊維強化材料) |
| 柔軟なエンジニアリング材料 | TPU | 柔軟性または弾性のあるレジン、純シリコン材料 | TPU、PP、Nylon 11 |
| スペシャルティ材料 | 複合材料 (炭素繊維、ケブラー、ガラス繊維) | 難燃性レジン、インベストメント鋳造材料、テクニカルセラミックス、ワックス複合材、歯科・医療用材料 | ナイロン複合材(ガラス充填または炭素繊維強化材料) |
用途に合った最適な材料選定をサポート
最適な材料は、用途や求める特性に応じて変わります。インタラクティブなマテリアル・セレクターで、常に拡大を続けるFormlabsの豊富な材料ライブラリからお客様の用途に最適な材料選定をサポートします。
SLA光造形3Dプリンタに関するFAQ
光造形3Dプリンタとは?
光造形方式は、3Dプリントの中でも最も人気のある方式です。1980年代に発明された、世界初の3Dプリント技術でもあります。それ以降、よりアクセスしやすい製品が登場したことでその導入と知名度は広がっていき、多岐にわたる数々の業界で設計や製造のプロセスを一新してきました。
SLA光造形プリンタは初心者にも向いていますか?
はい。フィラメント方式やSLA光造形方式の3Dプリントは、実は教育現場でも最も人気のある方式です。最初から最後まで包括的な手順で使いやすいこと、トレーニング資料が豊富なこと、そしてパーソナルサポートが可能なことが、FormabsのSLA光造形プリンタが初心者にも使いやすい理由です。
SLA光造形方式とフィラメント方式はどちらの方が優れているのですか?
お客様の用途や好みによって異なります。詳細は、フィラメント、パウダー、レジンを使った各方式の3Dプリンタを徹底的に比較したガイドをご確認ください。
Formlabs SLA光造形3Dプリンタを選ぶ理由は?
SLA光造形方式でプリントした造形品は、レジンを使う3Dプリント方式の中でも解像度や精度、ディテールの再現性、表面品質の滑らかさが最も高い仕上がりになります。また、標準・工学・産業用の熱可塑性樹脂に匹敵する様々な光学的・機械的・熱的な特性を備えた革新的なSLA用レジンが開発されているおかげで、どんな用途にも対応できる万能性もSLA光造形プリンタの特徴です。
SLA光造形方式は、成形型、原型、機能部品など、公差要件が厳しく、滑らかな表面品質が求められる繊細なディテールを持った試作品製作に最適です。また、SLA光造形方式は、工学用から製造業、歯科、ジュエリー、模型製作、教育分野における製品設計まで、様々な分野で幅広く使用されています。
SLA光造形プリンタの価格帯は?
SLA光造形プリンタの価格は、$300から$250,000以上と様々です。
- 低価格なものをお求めの場合、DIY向けやホビイスト向けの低価格SLA光造形プリンタが魅力的ではありますが、人の介入が多く必要な作業手順や安定性の低さ、使用できる材料の少なさなど、価格が安いことによるトレードオフも大きくなります。
- ミッドレンジのSLA光造形プリンタは、業界プロ向けの設計になっています。Form 3+は$2,499から、大容量SLA光造形プリンタのForm 3Lは$4,999からお買い求めいただけます。
- 受託メーカーなどで主に使用されている従来型の大容量工業品質SLA光造形プリンタは$100,000以上です。
FormlabsのSLA光造形3Dプリンタでサードパーティのレジンは使用できますか?
Formlabsでは、認可済みのサードパーティ製レジンとOpen Material Modeを提供しています。Open Material Modeとはオプションでプリンタごとにご購入いただけるライフタイムライセンスで、ライセンス付与後はFormabs認可済みのサードパーティ製レジンをすべてご利用いただけます。Open Platformの詳細はこちらからご確認いただけます。
SLA光造形方式による造形品の強度はどの程度ですか?
ご使用になる材料によって異なりますが、SLA光造形方式の造形品の強度は非常に高いと言えます。また、SLA光造形品は等方性を備えているため、X軸、Y軸、Z軸のどの方向に対しても同じ強度を持ちます。
Formlabsの材料ライブラリをご覧いただき、お客様の用途に最適な高強度エンジニアリング材料をお探しください。
SLA光造形方式による造形品の強度はどの程度ですか?
ご使用になる材料によって異なりますが、SLA光造形方式の造形品の強度は非常に高いと言えます。また、SLA光造形品は等方性を備えているため、X軸、Y軸、Z軸のどの方向に対しても同じ強度を持ちます。
Formlabsの材料ライブラリをご覧いただき、お客様の用途に最適な高強度エンジニアリング材料をお探しください。
SLA光造形品は防水ですか?
はい。SLA光造形方式による造形品は通常、防水性と気密性を備え、二次硬化後のレジンは吸水性が非常に低くなります。こちらの技術資料では、検証結果の詳細と、手頃な価格で水密エンクロージャを3Dプリントでカスタム製作するガイドラインをご紹介します。
FormlabsのSLA光造形3Dプリンタでサードパーティのレジンは使用できますか?
Formlabsでは、認可済みのサードパーティ製レジンとOpen Material Modeを提供しています。Open Material Modeとはオプションでプリンタごとにご購入いただけるライフタイムライセンスで、ライセンス付与後はFormabs認可済みのサードパーティ製レジンをすべてご利用いただけます。Open Platformの詳細はこちらからご確認いただけます。
レジンは安全に3Dプリントできますか?
一般的に、レジンの3Dプリントは安全に行えます。しかし、低価格レジンの中には頻繁な換気が必要なほど臭いが強かったり、よりリスクの高い化学物質が含まれているものもあります。Formlabsのレジンはいずれも、家庭用洗剤または接着剤と同等かそれ以上に安全な材料となるよう設計されています。Formlabsのレジン材料の取扱いについてはこちらをご確認ください。また、新しい材料をご使用になる場合は必ず安全データシートをお読みください。
レジンを使った造形品は二次硬化が必要ですか?
二次硬化の必要性はご使用になる材料によって異なりますが、二次硬化によって造形品の強度を最大限に高め、より安定した品質にすることができます。機能性レジンやスペシャルティレジンをご使用になる場合は特に、材料に備わる特性を最大限に発揮することが非常に大切です。生体適合性材料の場合、規制当局が定める安全基準を満たすために二次硬化は必須です。レジン製の造形品の二次硬化をお読みいただくか、SLA造形品の後処理および表面仕上げですべての作業手順をご確認ください。
FormlabsのSLA光造形3Dプリンタでサードパーティのレジンは使用できますか?
Formlabsでは、認可済みのサードパーティ製レジンとOpen Material Modeを提供しています。Open Material Modeとはオプションでプリンタごとにご購入いただけるライフタイムライセンスで、ライセンス付与後はFormabs認可済みのサードパーティ製レジンをすべてご利用いただけます。Open Platformの詳細はこちらからご確認いただけます。
FormlabsのSLA光造形3Dプリンタでサードパーティのレジンは使用できますか?
Formlabsでは、認可済みのサードパーティ製レジンとOpen Material Modeを提供しています。Open Material Modeとはオプションでプリンタごとにご購入いただけるライフタイムライセンスで、ライセンス付与後はFormabs認可済みのサードパーティ製レジンをすべてご利用いただけます。Open Platformの詳細はこちらからご確認いただけます。
FormlabsのSLA光造形3Dプリンタでサードパーティのレジンは使用できますか?
Formlabsでは、認可済みのサードパーティ製レジンとOpen Material Modeを提供しています。Open Material Modeとはオプションでプリンタごとにご購入いただけるライフタイムライセンスで、ライセンス付与後はFormabs認可済みのサードパーティ製レジンをすべてご利用いただけます。Open Platformの詳細はこちらからご確認いただけます。
